Not all organisms are multicellular, some organisms exist as just a single cell and are called a single-celled organism or a unicellular organism. Cells come together to form multicellular organisms like plants and animals and that is why we call cells, the building blocks of life.
However, in microbiology unicellular organisms are not like multicellular organisms that consist of multiple cells. Despite being smaller and single celled, these organisms can perform some of the same complex activities that multicellular organisms carry out.
Table of Contents
What is a single-celled organism?
A single celled organism is called a unicellular organism. This organism is made up of just a single cell and all its life processes are carried out in this single cell. Every single celled organism is able to survive because reproduction, feeding, excretion, and digestion all occur in one cell.
Examples of single celled organisms include bacteria, amoeba, protozoa, etc. These organisms are microscopic and can only be seen under a microscope. Nevertheless, there are some organisms that are partially unicellular, e.g Dictyostelium discoideum. Also, single-celled organisms can be multinucleate, such as Plasmodium, Caulerpa, and Myxogastria. The biggest single celled organism is Caulerpa taxifolia.
Furthermore, the majority of multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. For instance, gametes are reproductive unicells for multicellular organisms. Moreso, multicellularity seems to have evolved independently many times in the history of life. It is said that single-celled organisms are the oldest form of life with protocells possibly emerging 3.8 to 4 billion years ago.
The first single celled organism is called LUCA (Last Universal Common Ancestor) which probably existed around 3.5 billion years ago. Scientists believe that this one cell gave rise to all the subsequent life on earth. LUCA was one of the earliest prokaryotic cells in single celled organism evolution.

Types of single celled organisms (unicellular organisms)
- Prokaryotic organism
- Eukaryotic organism
Living organisms are classified into groups by scientists based on certain characteristics. In taxonomy, Domain is the highest rank level that can be divided into more specific kingdoms. Organisms are therefore classified into 6 kingdoms which include Animal, Plant, Fungi, Protista, Eubacteria, and Archaebacteria. Four of these six kingdoms are comprised of single-celled organisms. These four types of single celled organisms can further be divided into two groups:- prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. A single celled organism without a nucleus is called prokaryotic whereas a single celled organism is called a eukaryotic organism when it possesses a nucleus (see the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells).
Prokaryotic organisms
A prokaryotic organism is a single celled organism without a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. This means a single celled organism that lacks a nucleus is called a prokaryote. Prokaryotes are simple and have no membrane-bound organelles. The prokaryotic organism is just a simple single celled organism without membrane separating its organelles. They do not have a nucleus and so their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm in a single-celled organism and the circulatory system in a human both transport substances throughout the organism. All prokaryotic organisms are unicellular and organisms such as bacteria and archaea fall into this category.
Even though some prokaryotic cells live in colonies, they are not specialized cells with different functions. They may live together but each cell must carry out all its life processes in order to survive. This is different for even the simplest multicellular organism, which has cells depending on each other to survive. Since prokaryotic organisms do not have specialized organelles, they adapt to other ways of carrying out nutrition, reproduction, and waste excretion.
Characteristics of prokaryotes (single celled organisms that lack nuclei)
- Prokaryote is a single celled organism without a nucleus.
- These organisms are very small in size and vary from 0.1 to 5.0 µm. This size aids the diffusion of ions and molecules to different parts of the cell.
- The single celled organisms that lack nuclei have a peptidoglycan cell wall.
- These organisms use flagella for movement.
- The cell walls in prokaryotic organisms help to maintain the shape of the cell and prevents dehydration.
- These organisms have fimbriae for attachment to the host cell
- They also possess pili to exchange genetic material during conjugation.
Examples of single celled organism without a nucleus
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
Archaebacteria
The kingdom Archaeabacteria is an example of a single celled organism that lacks a nucleus. Initially, this kingdom was categorized as bacteria but scientists later discovered that they are unicellular microbes. These organisms are unique because they can thrive in conditions that few organisms can such as tundra and deserts. Hence, they are considered to be extremophiles because they thrive in extreme conditions. However, they still thrive in normal environments and can be found in soils, oceans, and the human colon.
The diversity of these organisms has allowed breakthroughs in both medicine and technology. For instance, a species called Pyrococcus can function in temperatures over 100°C. Hence, this species allows for food processing at extremely high temperatures, such as with whey and other dairy products. Other archaea bacteria species potentially hold the key to a new strain of antibiotics. They differ in structure from bacterial antibiotics and so are able to treat patients differently than the antibiotics typically prescribed now.
Eubacteria
The kingdom, Eubacteria is an example of a single celled organism that lacks a nucleus. Most single celled organisms in this kingdom are unicellular bacteria. Therefore, single celled organisms with cell walls but no nuclei are bacteria. These organisms can be considered as extremophiles found in extreme environments but they can also be found nearly everywhere on planet earth. Bacteria are not only associated with germs and diseases, most eubacteria are helpful and can be seen to aid with digestion in cheese, yogurt, and other foods.
Furthermore, bacteria are the basis of many antibiotics that are available today. Without antibiotics, the mortality rate of individuals will skyrocket for even the smallest ailment. For example is Erythromycin, a medication that is produced from good bacteria used to fight off bad bacteria. This antibiotic shuts down the protein production and replication in the bad bacteria.
Apart from medicinal uses, bacteria decompose dead and decaying matter for nutrients. Every living organism tends to benefit from this bacterial activity especially as industrialization advances and disasters occur. For instance, the bacteria Pseudomonas helps degrade oil spills in the ocean and on soils. While other bacteria help break down and clean up heavy metal contamination. They also treat harmful substances in the waste-water treatment process. The process whereby microorganisms are used to detoxify contaminants in the ocean, soil, or other environment is known as bioremediation.
Eukaryotic organisms
A single-celled organism with a nucleus is classified under eukaryotic organisms. Eukaryotes are unique and can be either a single-celled or multicellular organism. However, for any organism to be considered eukaryotic, it must have membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that stores the DNA as well as the mitochondria for energy and other organelles. The majority of eukaryotic organisms are multicellular but we still have some single-celled organism examples that fall into this category. Such unicellular organisms include protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi.
Characteristics of a eukaryote
- Eukaryote can be a multicellular or single celled organism with a nucleus
- These organisms are larger than prokaryotes and have a membrane-bound nucleus.
- The DNA of these organisms is present in the nucleus of the cell.
- Eukaryotes can be plant cells, animal cells, protozoa, or protists.
Examples of single celled organism with nucleus
- Protozoa
- Protista
Protozoa
A typical example of a single-celled organism with a nucleus is the Protozoa. The protozoa is a group of organisms under the kingdom Protista that come in many shapes and sizes. This phylum comprises only single-celled organisms that exist as free-living or parasitic organisms. These unicellular organisms like in different environments and have different functions. Examples of protozoans include the amoeba, sporozoans, Trichomonas vaginalis etc.
Some of these organisms are completely harmless whereas some exist as parasites and cause diseases. For instance, a common sexually transmitted disease caused by a single celled organism is Trichomoniasis. This disease is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, a flagellated protozoan parasite. Moreso, sporozoans are known to cause malaria.
Protista
A typical example of a single-celled organism with a nucleus is the Protista kingdom. This kingdom is divided into various groups that classify protists based on their movement, and how they obtain nutrition. Some protists are plant-like, animal-like, or fungus-like based on the characteristics they exhibit. Some of the most essential unicellular organisms such as euglena and phytoplankton belong to this kingdom.
List of single celled organism examples
- Bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Streptococcus, Pneumococci, etc
- Phytoplankton such as Diatoms and green algae
- Amoeba
- Sporozoans
- Euglena
- Yeast
- Slime mold
- Paramecium
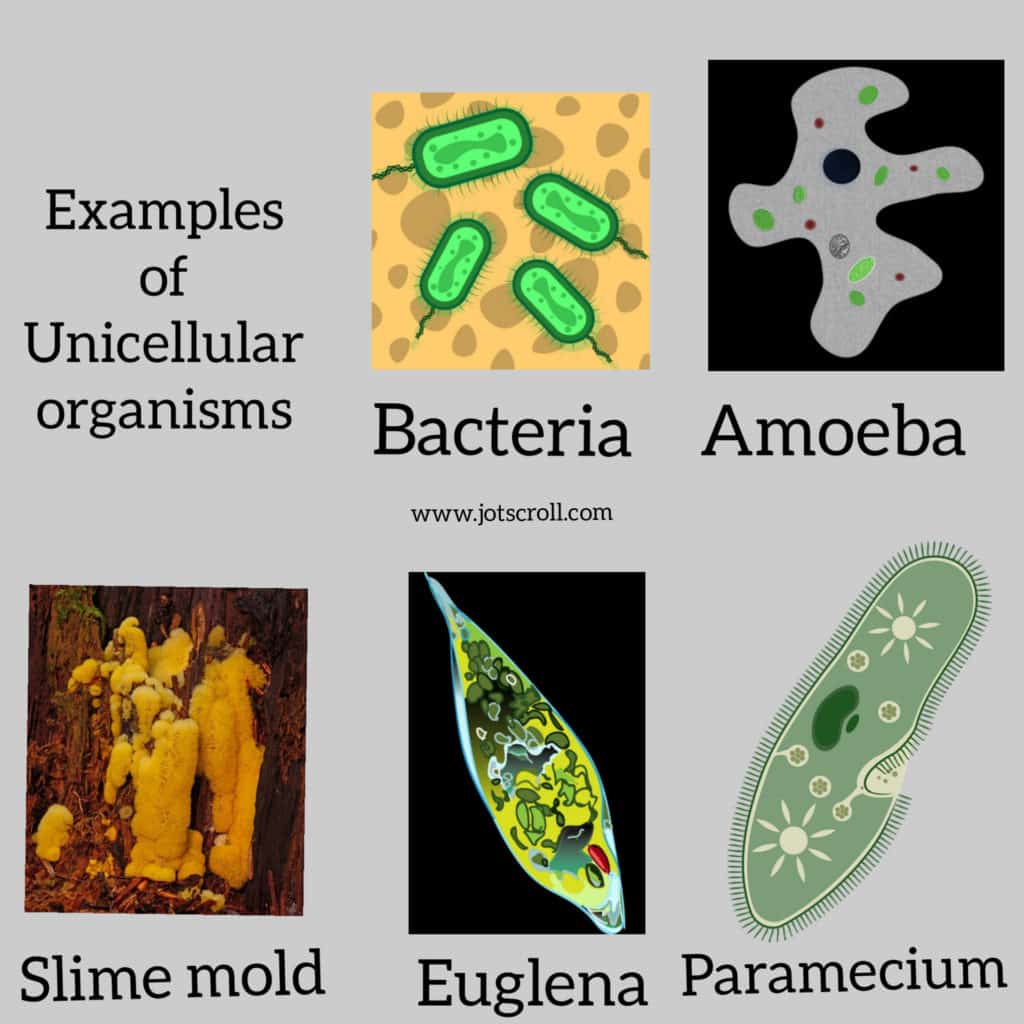
Bacteria
Bacteria are unicellular organisms that exist in millions. They are microscopic and can be found in every environment including inside organisms. The bacterium is also a single celled organism with flagellum for movement. Some bacteria can be harmful whereas some serve useful purposes. They support many forms of life and are also used in medicinal and industrial processes. Common bacteria examples include Escherichia coli, Streptococcus, Pneumococci, etc.
Phytoplankton
One of the single celled organism examples is the phytoplanktons. These organisms are unicellular protists that inhabit either salty or fresh aquatic environments. Some phytoplankton are bacteria but the majority are single-celled plant-like organisms. Two common examples of phytoplankton are diatoms and green algae.
Diatoms are significant because they produce a quarter of all the oxygen available. These organisms are similar to terrestrial plants because they carry out photosynthesis for chemical energy. In the process of photosynthesis, phytoplankton uses carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Under ideal conditions, the population of phytoplankton explodes into what we call bloom. These blooms are so large and can last long. Hence, providing most of the oxygen present on earth.
Depending on the species of diatom, these organisms make a glass-like transparent shell that varies in shape, pattern, and size. Even though they are unicellular, they can join together to form colonies. Thus, producing even more oxygen together. They form colonies in the shape of stars, ribbons, or even zigzags.
Amoeba
The amoeba is one of the examples of single celled organism. It is a type of harmless protozoa that lives in humans and moist environments such as decaying vegetation and wet soil. These unicellular organisms can be herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores. Amoeba feed on smaller organisms like bacteria living on rotting vegetation and tend to have good hunting skills. The amoeba is a shape altering single celled organism that possesses jelly-fish like tentacles, called pseudopodia. These organisms use their pseudopodia to touch and grab their prey. More so, they use these tentacles to move around. Once the amoebae engulf their prey, the enzymes inside it digest the prey and then get rid of the waste by pushing it back through the membrane.
Sporozoans
The sporozoans are one of the single celled organism examples.These organisms are a type of protozoa that are very parasitic. Sporozoans are known to cause malaria in birds and mammals. The already infected mosquitoes as hosts, inject sporozoans into the bloodstream, causing malarial infection. Today, the majority of people suffer from malaria than any other disease, especially in Africa where the warm conditions aid the growth and contagion of the parasite.
Euglena
The euglena is another single celled organism with flagellum. These organisms are like a unicellular plant-animal hybrid. This single celled organism under a microscope appears to have a teardrop shape. Like plants, euglenas can make their own food, but they can also feed like an animal. When there is no enough light for photosynthesis. These organisms feed on green algae. This is why most euglenas are green. Furthermore, when euglena carries out photosynthesis, the resulting oxygen emission is equal to that of phytoplankton.
Yeast
The yeast happens to be one of the few unicellular organisms that fall into the Kingdom Fungi. This unicellular organism is mostly found in sugary areas, such as fruits and flower nectar. There are different species of yeast, and many are used to make beer, bread, and wine. For example, the yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae is a single celled organism that ferments sugar into carbon dioxide and alcohol. As a result, it is commonly used in the baking and brewing industries. Recently, yeast has been manipulated to produce ethanol too, leading to new innovations and ideas in environmental fuel sources.
Slime mold
The slime mold is one of the examples of single celled organism. For many years, these single-celled organisms were considered fungi until scientists discovered they were completely unrelated to fungi. These unicellular organisms swarm together to form one giant cell-like structure with several nuclei.
Paramecium
The paramecia are examples of single celled organisms found in freshwater environments. This organism is a well-known genus of ciliate protozoa and belongs to the kingdom Protista. As protists, the paramecium is a single celled organism that reproduces asexually. This unicellular eukaryotic organism has a shape that resembles the sole of a shoe. Its size ranges from 50-300um which varies based on species.
Characteristics of a single-celled organism
- In order to identify a specific structure in a single celled organism, the single celled organism has to be viewed under a microscope.
- Single celled organisms reproduce asexually.
- They can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
- A single celled organism can be found in almost all habitats from frozen tundra to hot springs.
- These organisms possess whip-like structures for movement.
- They obtain and release nutrients through the process of diffusion.
- A single celled organism dies regularly from killing itself in reaction to stresses it might have survived.
- In single celled organisms materials are stored primarily in the vacuoles.
Nutrition
A single celled organism is able to feed on other organisms or liquid matter through certain processes. They ingest and feed on larger particles via phagocytosis or pinocytosis. While smaller-sized particles enter into the organisms via osmosis and diffusion. Most single celled organisms live in the water and have to move around to find food while some organisms like the plant-like protists manufacture their own food. In single celled organisms materials are stored primarily in the vacuoles
Reproduction
Just as multicellular organisms, a single celled organism is able to reproduce as well. The majority of single celled organism reproduction occurs asexually where cell division is used as a means of reproduction. Unicellular organisms like bacteria, amoeba, and archaea reproduce through binary fission. This type of asexual reproduction occurs when a single celled organism divides into two organisms. Hence, giving rise to two daughter cells.
Yeast cells reproduce via mitosis and many of them use a process known as budding. In budding, most of the cytoplasm is held by the mother cell. Sometimes, the single celled organism amoeba can reproduce through a process called encysting. The amoeba forms a protective covering around itself during unfavorable conditions. This protective covering is called a cyst and contains chitin that helps it to reproduce.
Furthermore, though protozoa mainly reproduce via asexual reproduction, some species reproduce sexually. The protozoa with sexual abilities are pathogenic and include species such as Giardia duodenalis, Plasmodium falciparum, Toxoplasma gondii, Leishmania species, and Trypanosoma brucei.
Respiration
During gas exchange, the cell membrane of a single celled organism is used in the process of diffusion. Unicellular organisms do not have any respiratory structure, thus, respiration in single-celled organisms occurs through their cell membrane or general body surface. An exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place through the body surface or cell membrane via the process of diffusion. These organisms, therefore, respire aerobically or anaerobically through diffusion, the movement of a substance from a higher concentration to a lower concentration.
Death
Apoptosis (or programmed cell death PCD) is an evolutionary conundrum. This is a regulated process of a cell killing itself. In reaction to stresses they might have survived, single celled organisms kill themselves regularly. Some single-celled organisms such as fungi, red algae, green algae and even bacteria have genetic programs that when activated cause self-destruction to the organism itself. These suicidal cells actively expend energy in order to shrink, chop up their own DNA and cause other fatal changes to themselves. Hence, the single celled organism dies.
Importance and significance
Every single celled organism is able to survive because it carries out reproduction, feeding, excretion, and digestion in one cell. The majority of single-celled organisms inhabit extreme environments like hot springs, polar ice, thermal ocean vents, and frozen tundra. Such single-celled organisms are called extremophiles. This type of single celled organism that can live in extreme environments is resistant to extremes of pH or temperature. They are adapted to survive in habitats that multicellular organisms can’t survive.
This characteristic has made scientists use them in various ways. For instance, a water sample from a hot thermal vent contained a single-celled organism called Thermus aquaticus. When Thermus aquaticus was discovered in the boiling water of a Yellowstone Park hot spring, scientists used the special enzyme TAQ polymerase of this organism. This special enzyme was used to replicate DNA billions of times in the span of a few hours. This discovery was useful for forensic science and genetic testing. Moreso, other single-celled organisms that can live in extreme environments have been used in the treatment of arthritis and autoimmune diseases, treatment of waste, making paper, as well as radiation resistance.
Nevertheless, not all single-celled organisms are extremophiles. Some of them live in the same narrow range of living conditions as multicellular organisms. Even in living under such conditions, they produce things that are necessary to all forms of life on earth. For example, phytoplankton is a single-celled organism that lives in the ocean. These organisms are the foundation of the ocean’s food chain. Also, they provide the majority of the oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere. Without oxygen, other life forms such as animals and plants would cease to exist.
FAQs
What is a single celled organism called?
A single celled organism is also called a unicellular organism.
What is a single celled organism without a nucleus?
A single celled organism without a nucleus is called a prokaryotic organism or prokaryote.
What is the largest single celled organism?
The Caulerpa taxifolia is known as the world’s largest single celled organism. This organism is a form of seaweed which are capable of reaching 10ft or more in length. They are single cells that possess many different nuclei.
These organisms are highly invasive and negatively impactful for other organisms and even humans. The Caulerpa taxifolia is very hardy and can survive out of water for days. It can reproduce from small pieces of the whole organism.
What is the biggest single celled organism?
The biggest single celled organism the Caulerpa taxifolia, a form of seaweed.
Is an amoeba a single celled organism?
Yes, amoeba is a single celled organism. This organism is a type of harmless protozoa that lives in humans and moist environments such as decaying vegetation and wet soil.
Is algae a single celled organism?
Algae range from microscopic and unicellular (single-celled) to very large and multicellular. Not all algae are single-celled. Diatoms and golden-brown algae are the most widespread single-celled species of algae.
How does a single celled organism grow?
In single celled organism, reproduction is closely associated with growth. Growth happens to be a stage in the process of their reproduction. Growing for these organisms involves a stepwise and ordered increase in the size of the cytoplasm as well as an increase in the number of organelles.
What single celled organism causes malaria?
Malaria is caused by the single-celled protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium. These causative agents include Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax; Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae.
Is fungi a single celled organism?
Not all fungi are single-celled, the majority are multicellular. Yeasts are the known unicellular fungi.
How does a single celled organism maintain homeostasis?
These organisms grow, transform energy, respond to the environment and reproduce in order to maintain homeostasis.
What is the single celled organism that is animal and plant like called?
The Euglena
Is plankton a single celled organism?
Majority of planktons are single celled while some are multicellular.
What does a single celled organism look like?
They are microscopic in size and varies in shape and structure.
When did the first single celled organism appear?
Roughly about 3.5 billion years ago
Is bacteria a single celled organism?
Yes. The single celled organisms with cell walls but no nuclei are bacteria.
How does an amoeba survive as a single celled organism?
Amoeba feed on smaller organisms like bacteria living on rotting vegetation and tend to have good hunting skills. The amoeba is a shape altering single celled organism that possesses jelly-fish like tentacles, called pseudopodia.
These organisms use their pseudopodia to touch and grab their prey. More so, they use these tentacles to move around. Once the amoebae engulf their prey, the enzymes inside it digest the prey and then get rid of the waste by pushing it back through the membrane.
How are materials transported in a single celled organism?
A single-celled organism relies on diffusion to transport materials into and out of the cell.
What is a single-celled organism with a nucleus called?
A single celled organism with nucleus is called a eukaryotic organism.
How does a single celled organism survive?
These organisms have everything that they need to survive within their one cell. Single-celled organisms are able to get energy from complex molecules and can sense their environment. The organism’s ability to perform various functions is part of their organization.
Why is an amoeba considered a single-celled organism?
The amoeba is one of the examples of single celled organism. It is a type of harmless protozoa that lives in humans and moist environments such as decaying vegetation and wet soil
What is an example of a single celled organism?
Diatoms, euglena, bacteria, yeast, slime mold etc are all examples of single-celled organisms.
What is another word for a single celled organism?
Single celled organisms are also called unicellular organisms.