Table of Contents
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which carbon dioxide from the air is fixed into organic molecules and it helps to produce over 99% of food for living organisms. The light energy is converted to chemical energy. During this process, plants absorb CO2 and release O2 as a byproduct. The components required for this process are Light, Chlorophyll, Water, and Carbon dioxide (CO2). The process occurs in green plants in an organelle known as the Chloroplast.
Meaning
The photosynthetic process involves the trapping (fixation) of carbon dioxide and its subsequent reduction to carbohydrate, using hydrogen from water; such a biochemical reaction by which chloroplast, in the plant cell, uses the energy received from the photon of sunlight to manufacture carbohydrate food by CO2 of the atmosphere and water and other organic substances in the cell is useful not only to plant alone but also to animals.
Definition
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process whereby green parts of plants manufacture carbohydrate food by the use of CO2 and water with the help of energy obtained from sunlight. It occurs through two series of reactions: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle (also known as the light-independent reactions)
Only certain organisms, called photoautotrophs, can undergo the photosynthetic process; they require the presence of chlorophyll (a plant pigment), a specialized pigment that absorbs certain portions of the visible spectrum and can capture energy from sunlight. The photosynthetic process uses carbon dioxide and water to assemble carbohydrate molecules and release oxygen as a waste product into the atmosphere. Eukaryotic autotrophs, such as plants and algae, have organelles called chloroplasts in which photosynthesis takes place, and starch accumulates. In prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, the process is less localized and occurs within folded membranes, extensions of the plasma membrane, and in the cytoplasm.
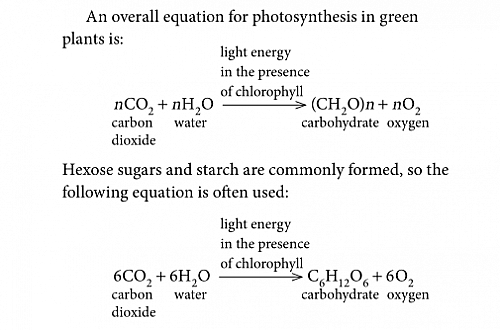
Chemical Equation of Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 12H2O —–> C6H12O6+ 6O2+6H2O
The above equation shows the balanced chemical equation of Photosynthesis
Photosynthetic organisms
Organisms that synthesize their own food using the process of photosynthesis are called Photoautotrophs; these photosynthetic organisms include green plants, photosynthetic prokaryotes, and both single-celled and many-celled Protoctists (including the green, red and brown algae). There are other Autotrophs (organisms that make their own food directly) that do not use photosynthesis; they use chemical energy sources and are called Chemoautotrophs.
Photosynthesis Process
The process of photosynthesis convert light energy into chemical potential energy of organic molecules which can then be released for respiration. Almost all the energy transferred to all the ATP molecules in all living organisms is derived from light energy used in photosynthesis by autotrophs.
In explaining the photosynthetic process, it is important to know that there are two reactions the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis and the light-independent reaction (also known as the dark reaction).
Photosynthetic Reactions
The two reactions are the light-dependent reaction, for which light energy is necessary, and the light-independent reaction (or Calvin cycle or Dark reaction), for which light energy is not needed. Light energy is also needed to provide chemical energy in the form of ATP, for the reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrate in the light independent reactions.
The light reaction
The light reaction stage occurs during the day or in the presence of sunlight. The light energy or solar energy is captured by the chlorophyll and electrons are excited. The energy so trapped is used to split water into a hydrogen ion (H) and hydroxyl ion (OH). This splitting of water into a hydrogen ion (H) and hydroxyl ion (OH) is known as the photolysis of water.
During this process, oxygen is given out as a by-product at the same time, a compound, co-enzyme, or NADP is reduced by hydrogen ion to NADPH, and ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is also formed.
The light dependent reactions include the splitting of water by photolysis to give hydrogen ions (protons) and the synthesis of ATP in photophosphorylation. The light-dependent reactions only take place in the presence of suitable pigments that absorb certain wavelengths of light. Light energy is necessary for the splitting (photolysis) of water into hydrogen and oxygen; oxygen is a waste product in this reaction.
The dark reaction or Calvin Cycle (or the Light-independent reaction)
In this process there is a fixation of carbon dioxide; the carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon sugar, ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), to give two molecules of a three-carbon compound, glycerate 3-phosphate (GP); this compound is also sometimes known as PGA. GP, in the presence of ATP and reduced NADP from the light-dependent stages, is reduced to triose phosphate (TP), a 3-carbon sugar. This is the point at which carbohydrate is produced in photosynthesis
The dark reaction of Photosynthesis occurs at night or in the absence of light, it is also called the Calvin Cycle. Together with the energy provided by ATP: the reduced compound Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NADP) then lead to the assimilation of carbon dioxide. Through a series of steps, each controlled by a specific enzyme, a three carbon compound (CH2O) or sugar is formed. The formation of this 3-carbon compound can be represented by a chemical equation as follows:
The Calvin Cycle

Calvin Cycle of Photosynthesis (Dark Reaction)
CH20 is the carbon structure from which simple sugar, fat, and oil, protein etc are formed during the dark reaction.
Reactants in the photosynthetic process
- Carbon dioxide, CO2
- Water, H2O
- Light energy
- Presence of chlorophyll (Photosynthetic pigment)
What is needed for photosynthesis?
- Carbon(IV)oxide: Carbon(IV)oxide is derived from the atmosphere and it diffuses into the intercellular spaces through the stomata of the leaves. From the intercellular spaces, carbon(IV)oxide diffuses further into the mesophyll cells containing chloroplast.
- Water and Mineral salts: Water and mineral salts are derived from the soil. They pass into the roots of plants through the root hairs by a process called Osmosis. Water and dissolved mineral salts are conducted by xylem from the roots through the stem and finally to the mesophyll cells containing chlorophyll of the leaves.
- Sunlight: Sunlight is obtained from solar energy. The light from the sun is trapped by the chlorophyll of the leaves. The sunlight is used to split water into hydrogen ion and hydroxyl ions in a process called Photolysis.
- Optimum Temperature: Temperature is derived partly from the solar energy and partly from chemical reactions within the leaves during which heat is generated. A suitable temperature is important for enzymes to enable them to function properly during photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll: Chlorophyll is the green coloring pigment found in the palisade and spongy mesophyll of the leaves. The chlorophyll represents sites where food can be synthesized and it helps to trap solar energy and convert it to chemical energy
Factors affecting Photosynthesis
There are many factors needed for photosynthesis, these include carbon dioxide, water, light energy and photosynthetic pigment. Some of these factors together with external factors affect the rate of photosynthesis.
The main external factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis are light intensity and wavelength, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration. At constant temperature, the rate of photosynthesis varies with the light intensity, initially increasing as the light intensity increases.
However, at higher light intensities, this relationship no longer holds and the rate of photosynthesis reaches a plateau; also, at a high light intensity, the rate of photosynthesis increases as the temperature is increased over a limited range. At low light intensity, increasing the temperature has little effect on the rate.
Photosynthesis Steps
- In photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments and converted to chemical energy, which is used to produce complex organic molecules.
- In light-dependent reactions, water is split by photolysis to give hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen.
- The hydrogen ions and electrons are used to reduce the carrier molecule, NADP, and the oxygen is given off as a waste product.
- ATP is synthesized in the light-dependent reactions of cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. During these reactions, the photosynthetic pigments of the chloroplast absorb light energy and give out exciting electrons.
- Energy from the electrons is used to synthesize ATP. ATP and reduced NADP are the two main products of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis, and they then pass to the light independent reactions.
- In light-independent reactions, carbon dioxide is trapped by combination with a 5C compound, RuBP, which acts as an acceptor molecule. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco), which is the most common enzyme in the world. The resulting 6C compound splits to give two molecules of a 3C compound, GP (also known as PGA).
- GP is reduced to carbohydrate, using ATP and reduced NADP from the light dependent reactions. This carbohydrate can be converted into other carbohydrates, amino acids and lipids or used to regenerate RuBP. This sequence of light-independent events is called the Calvin cycle.
Products of Photosynthesis
The products of photosynthesis are carbohydrates and oxygen. Oxygen is a waste product in photosynthesis.
Importance
- Production of Food: Photosynthesis provides food for both plants and animals. All green plants are able to manufacture their food through the process of photosynthesis while animals depend directly or indirectly on the green plant for their food.
- Purification of the Atmosphere: Waste products like carbon(IV)oxide released during respiration by both plants and animals are removed from the atmosphere by plants for use during photosynthesis.
- Release of Oxygen to the Environment: Oxygen needed for respiration by plants and animals is released into the environment during photosynthesis.
- It serves as building blocks for other substance: Photosynthesis provides the building block or carbon skeleton on which other food substances such as proteins, fats, oil etc are built.
Facts
- There are two types of reactions that can occur in Photosynthesis, which are light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions.
- Though Photosynthesis requires light energy, it can occur even in the dark.