Lifestyle changes or lifestyle modification refers to the adoption and practice of attitudes and habits (healthy behaviors) that promote healthy living and enhance wellness. Healthy living refers to regular display of healthy behaviors leading to promotion of optimum health of an individual.
There are two things that determine how long and how well you will live, which are: genetic factor and your lifestyle. Lifestyle is the single most important determinant of both quality of life and longevity especially as you grow older. The leading causes of death in both developed and developing countries are linked to negative lifestyle practices or changes.
Table of Contents
What is Lifestyle?
In sociology, a lifestyle is the way a person lives; in public health, lifestyle generally means a pattern of an individuals behavioral choices and practices that lead to elevated or reduced health risk.
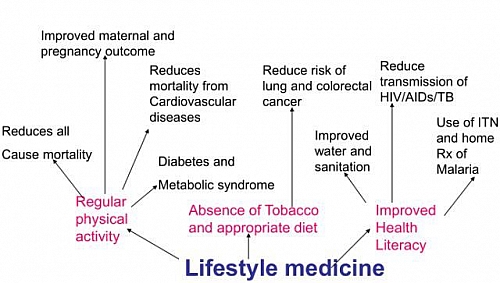
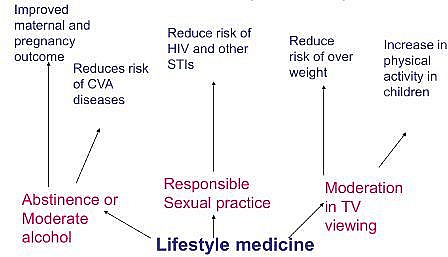
Lifestyle Medicine
Lifestyle Medicine refers to integration of lifestyle practices into the modern practice of medicine both to reduce risk factors for disease and where disease is present, to serve as adjunct to its therapy and control.
The leading causes of Mortality in the United States of America include:
- Cardiovascular diseases such as Myocardial infarction (MI) which could be due to high cholesterol level in the blood.
- Cancer
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases mostly caused by smoking of cigarettes.
- Accidents
A healthy person should be physically fit and full of vitality and the person should be happy, demonstrates emotional resilience and shows both normal health and biochemical markers. The fitness of an individual can be assessed in a number of ways which are described below.
Ways to assess fitness
- Physical health markers such as Anthropometry and amount of physical activity level carried out daily by an individual
- Biochemical health markers such as blood glucose, lipids (such as cholesterol level), hormones, proteins and electrolytes.
Use of Anthropometry in assessment of Fitness
- Body Mass Index (BMI): This shows whether you are underweight, have obesity or normal in weight. If your BMI is above 25, your risk of having cardiovascular diseases begins to increase. The Normal BMI is within the range of 18.5-24.9 kg/m2
- Others include the Waist-HIP ratio, Vital capacity, body fats (of which the normal should be 15 to 23% of bodyweight), temperature and blood pressure which shows in you have hypertension or not.
Assessment of fitness using the physical activity level
- Daily number of footsteps taken by the individual
- Daily time spent on physical activity or exercise
- Cardio respiratory endurance
Use of Foot steps
- Less than 5000 footsteps daily is regarded as Sedentary lifestyle
- From 5000 7499 footsteps per day is regarded as Low active lifestyle
- From 7500 to 9999 footsteps is known as Some what active
- Walking 10000 to 12499 footsteps is an Active lifestyle
- Someone who walks more than 12500 footsteps a day is regarded as Highly active
Use of Physical activity or exercise for assessment of lifestyle behavior
30 minutes of daily physcial activity or moderate intensity exercise at least five times weekly such as walking, gardening, dancing, etc or 20 minutes of high intensity exercise 3 times per week such as running, jogging, cycling, dancing, or pushups is recommended for healthy lifestyle.
Dietary healthy lifestyle
Choice of type of diet has been linked to overall mortality. What you eat has implications on health. Some foods are good while some are harmful for the body. The more the cholesterol content of food such as in red meat, the more harmful or the more the risk of atherosclerosis; hence eating red meat is dangerous to health. To make it simple to understand, the more the number of limbs or legs an animal has, the more harmful the meat can be to health. Cows, goats, sheep or buffalos have four legs, when compared to chickens with 2 legs; a chicken is preferable than the animals with 4 legs. On the other hand, comparing fish without legs and chicken, eating Fish is better than eating chicken. This is the simple illustration that any child or non-medical individuals can understand.
Vegetarians feed mainly on plant based food and some of the vegetarians add little amount of animal protein to provide for the basic needs of the body, depending on the type of animal protein added; vegetarians can be group as:
- Lacto-Vegetarians: they add dairy product to their diet
- Ovo-Vegetarians add to their meals, eggs as source of animal protein
- Ovo-Lacto Vegetarians add both eggs and dairy products to meals
- Pesco Vegetarians add only fish to the diet
- Semi-vegetarians take meat once a week
Non-Vegetarians (include meat in their diet)
How People Change (Transtheoretical Stages of behavior change)
- Pre-contemplation
- Contemplation
- Preparation
- Action
- Maintenance
- Termination/adoption
Understanding Stages of behavior Changes in lifestyle modification
The following statements will help you understand the different stages that an individual undergo in lifestyle changes.
Scenarios that depicts different stages of the change process
- I smoke cigarette and I do not see the need to stop it ( this person is the pre-contemplation stage)
- I currently smoke cigarette but I am considering dropping this habit in the next 6 months (contemplation stage)
- My current alcohol intake is high but I have plans to reduce it to two drinks daily by next month (Preparation stage)
- I have been exercising regularly but I have done so only in the last six months (Action stage)
- I currently take four servings of vegetable daily and I have done that for more than six months now (Maintenance stage)
- I currently meditate daily and I have done so for over five years now (Termination stage and hence, the person has successfully modified such lifestyle).
Personal Wellness Plan
One way to learn lifestyle medicine fast is to practice it using the personal experience approach. Those that practice lifestyle medicine find it easy to prescribe it to their patients and do have the best of results. Have your personal wellness plan and address key issues that keep one fit and happy.
Personal wellness plan key issues
- Exercise
- Diet and nutrition including the use of water
- Sleep and Rest
- Spirituality
- Hygiene (personal, mental, environmental)
- Sexuality
- Emotional resilience
- Relationship management
- Humour (laughter, smiles, jokes,)
- Use of preventive health services such as immunization, screening services for cancers, ocular problem, hepatitis B and many more
What do you need to avoid?
- Tobacco use (cigarettes, chewing of tobacco)
- Substance abuse (drugs and other chemicals)
- Excessive alcohol
Implementing the Wellness Plan
- Assess your strength and weakness with respect to the key issues mentioned above
- Identify the habits or the unhealthy behavior you intend to change with respect to the key issues
- Assess readiness to change in relation to each unhealthy behavior
- Identify those habits or unhealthy behaviors that you are willing to change
- Assess your experience with attempt to change a habit in the past and outcome
- Start with the most easy to change habit (based on level of confidence) or behavior
- Through the use of SMART goals, adopt, practice and maintain a healthy lifestyle
S: Simple; M: Measurable; A: Achievable; R: Relevant; T: Time bound goals
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is a life-long practice. It takes between 18 to 66 days to develop a new habit/behavior and 5 years to integrate it. As one achieves a particular habit the chances of success in subsequent ones increase; it is good to start with a behavior that has a wide range of benefits such as exercise.