Table of Contents
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a serious infection affecting the liver that causes inflammation of the liver cells. Hepatitis C is also called Non A, Non B hepatitis. The Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and belongs to a group of viruses known as Flaviviridae Family. The Hepatitis C virus is infectious but not contagious because it can be transmitted to another person by blood but not by direct physical contact or closeness with an infected person.
Hepatitis C incubation period is about 14 days to 160 days, which refers to the time it takes to show the first symptom. It occurs often in males than females and affects people of age 30 to 49 years in developed countries. About 3.2 million persons in the United States have Chronic Hepatitis C which makes this a common infection of blood in the United States. Hepatitis C is a leading cause of Liver cancer and also a leading cause of Liver transplants in the world.
Hepatitis C Transmission
- Intravenous (IV) drug users
- Sexual intercourse, especially homosexuals
- Blood transfusion
- Mother to child transmission
- Piercing of the body such as tattooing
- Organ transplants from infected persons
- Exposure to the virus during long term dialysis for Kidney disease
The risk of spread of Hepatitis C is increased in disease conditions such as HIV/AIDS, Vaginal infections, Sexually transmitted Diseases/Infections (STDs/STIs). It is not transmitted by saliva, hence, kissing does not cause Hepatitis C unless you and the partner have bleeding gums. Coughing, sneezing, eating together with an infected person does not transmit Hepatitis C and hugging does not transmit it too.
A pregnant woman with Hepatitis C can transmit it to the baby; if the mother is negative and the father is positive, the baby in the womb will not have Hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C symptoms and signs
- Influenza-like symptoms such as sore throat, fever, muscle pains, runny nose and headaches
- Joint pains (arthritis)
- Anemia (aplastic anemia)
- Vomiting (throwing up)
- Abdominal pains
- Fatigue (tiredness)
- Feeling of being sick
- Yellow eyes and skin (jaundice)
- Most people infected with Hepatitis C do not even show symptoms
Symptoms of Hepatitis C are the same as that of other Hepatitides (plural of hepatitis). Their symptoms are similar and use of symptoms alone cannot point whether you have Hepatitis A, B, C, D or E and it can only be confirmed by laboratory investigations (tests).
Hepatitis C diagnosis
As early as 2 weeks of being infected with Hepatitis C virus, the RNA can be detected in the blood by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR); the Antibodies can be detected after 12 weeks by serology. Sometimes the blood of one patient might be mistaken as the blood specimen for you, in this instance, the Hepatitis C test will be a false positive result because it will show you have Hepatitis C while you do not actually have it. The RNA test measures the viral load and is also called the Viral load test for Hepatitis C.
The Hepatitis C disease slowly progresses to end stage liver disease in a period of about 20 to 40 years from time of infection with the virus.
A non-reactive Hepatitis C screening test (negative antibody) shows that you do not have the Hepatitis C infection.
A positive Hepatitis C antibody test (Reactive ) shows the Hepatitis C antibodies were found in your blood and this means you have been infected at some point in your life but it does not mean that you currently have an active (on going) infection. The single confirmatory test is the PCR mentioned above.
Hepatitis C treatment drugs
About 6 drugs are used for treatment of Hepatitis C and it can be totally cured with the virus cleared from the body. Not only can Hepatitis C be cured but treatment also helps in prevention of transmission to others. The limitation to treatment is that it is very expensive and treatment of Hepatitis C may last for 8 to 12 weeks. The drugs used for treatment of Hepatitis C include:
- Standard interferon (IFN) or pegylated interferon alpha (PEG-IFN)
- Ribavirin (RBV)
- Protease inhibitors (PIs) such as boceprevir, telaprevir and simeprevir
- Nucleotide analog polymerase inhibitor such as sofosbuvir
These drugs are highly toxic and side effects are mentioned below.
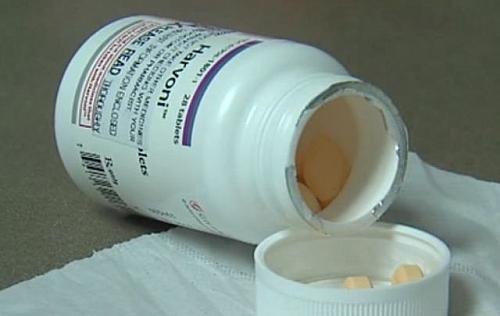
Some brand names for treatment of Hepatitis C include: Harvoni drug, which can cure Hepatitis C within 8 to 12 weeks but the downside is that the drug costs about 1000 dollars per pill and for the 12 week treatment; you will need a minimum of about 84,000 dollars which may not be affordable to many of those who need treatment for Hepatitis C. The treatment of Hepatitis C is very expensive.
Hepatitis C drugs side effects
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Thyroid problems
- Changes in sight or vision
- Diarrhea
- Low white blood cells
- Rash
- Nausea
- Difficulty in falling or staying asleep
- Itching
Hepatitis C prevention
- Avoid sharing of needles
- Drinking of alcohol worsens Hepatitis C infection but it is not a cause of Hepatitis C but it is a cause of Hepatitis.
- Eat a healthy balanced diet
- Routine screening of blood during blood donation to prevent transmission to people that will be transfused with the collected blood
There is currently no vaccine for Hepatitis C and it will be best to prevent getting infected with this virus. Vaccinations against Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B do not offer protection against Hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C complications
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) which refers to cancer of the liver
- Liver Cirrhosis
- Liver failure
- Chronic active Hepatitis
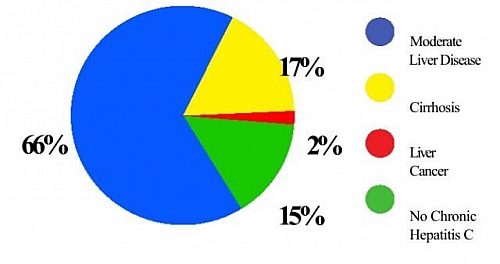
Some people when infected can get rid of this virus but others may not, the unfortunate thing is that the majority may not be able to get rid of the virus and may develop the complications of Hepatitis C. Out of 100 people infected by Hepatitis C virus; about 85 may develop chronic infection. For every 5 out of this 85, one person may progress to develop liver cirrhosis which may lead to liver cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma). Hepatitis C does not cause acute fatty liver disease.
Clarification of misconceptions about Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is singly caused by a virus. This microbe (tiny organism that cannot be seen with the eyes) can only be viewed with the aid of an electron microscope. There are other pathogens (microorganism that cause disease) that can cause Hepatitis. Hepatitis includes both the ones caused by viruses and other causes such as Alcohol, drugs, parasites and afflatoxins. It is therefore a misconception to think of Hepatitis C as being the same as Hepatitis.