Table of Contents
What are hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids refer to bulging of the blood vessels around the anus that may protrude out of the rectum with accompanying bleeding. Hemorrhoids are the commonest cause of bleeding from the rectum (anus) and the bleeding mostly occurs as a result of prolapse of the hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids may occur within a short time (acute) or may be small in size and takes a long time to heal (chronic). The acute hemorrhoids may become dangerous to health whereas the chronic hemorrhoids may cause iron deficiency anemia. Hemorrhoids are also known as Piles; these words are derived from the common symptoms of this disease which are bleeding from the anus and protrusion.
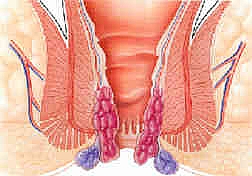
Understanding hemorrhoids requires you know how the anatomy of the anal canal is and the terms necessary for description of this ailment. Whether you are a medical professional or not, without a proper knowledge of the structures of the anus, you may just be confused and be left with a poor mental picture of what hemorrhoids are and how to get rid of them. A picture of the anal canal is show to aid in understanding.I will be discussing this starting with the normal anatomy of the anus (the picture is shown above), the pathophysiology (how it starts) and how to cure them.
There are blood vessels around the anus that consist of arteries and veins. The veins form a network around the anal canal known as plexus which are embedded in fats and together, the fats and veins and other structures are known as the hemorrhoidal tissue. When the veins become engorged with blood due to some precipitating factors mentioned below, they bulge and may protrude through the anus together with the other structures of the hemorrhoidal tissue and this is what is then called hemorrhoids.
What causes hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are caused by bulging (dilatation) of the veins of the anal canal. These veins become engorged with blood due to some predisposing factors. If you have any of the predisposing factors to hemorrhoids, it does not mean that you must have it, all it means is that these factors make it easy or likely for you to have the disease. The risk factors are listed below.
Predisposing factors to getting hemorrhoids
- Hereditt: if your any of your parent has it, then you are likely to have hemorrhoids
- Pregnancy
- Age
- Obesity
- Puerperial period (the first 6 weeks after giving birth) predisposes a woman to hemorrhoids
Precipitating factors of hemorrhoids
- Constipation
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Anal spasm
- Infection
- Enemata
- Any cause of a rise in intra-abdominal pressure
Pathophysiology of hemorrhoids
When feces become hardened and you attempt to expel it, it causes congestion of the network of veins in the internal hemorrhoidal tissue; the compression of this tissue cause progressive mucosal prolapse with every movement of the bowel making the hemorrhoid to come out until it develops fully into external hemorrhoids. In pregnancy, hemorrhoids develop even before the pregnancy becomes large and the reason is unknown.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids
- Passage of stool with blood that is bright red in color and usually not mixed with the stool. The blood may just be streaks on the stool or may be much that may lead to anemia. Hemorrhoids are the commonest cause of anemia in men.
- Prolapse (protrusion of the hemorrhoidal tissue)
- Mucous discharge: this increases as the prolapse increases
- Irritation of the anus such as itching and pains
Physical signs of hemorrhoids on examination
The doctor makes the patient to lie on the back while the hemorrhoid is examined. By assuming the anus to be like a clock, the common positions of the hemorrhoids are in the 3 oclock position, 7 oclock and 11 oclock. Parting of the anal opening may reveal associated anal fissure.
The visualization of the hemorrhoids is done by a process known as Proctoscopy, using an instrument known as a Proctoscope that is inserted into the anus.
Types of hemorrhoids
- First degree hemorrhoid: this type of pile hardly comes out but with straining, it may come out and returns back even without pushing it with your hands. It may not be seen because it occurs inside.
- Second degree hemorrhoids: in these, the hemorrhoids come out but spontaneously return back.
- Third degree hemorrhoids: these piles prolapse (come out) but need to be pushed with the fingers to return into the anus
- Fourth degree hemorrhoids: these types become permanently prolapsed and cannot be pushed back.
Classification of Hemorrhoids
- Internal hemorrhoids
- External hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids occur high up in the anal canal and are not visible whereas external hemorrhoids are visible and occur outside the anus. The external hemorrhoids are seen basically as ballooned skin appearing blue in color.
Complications of hemorrhoids
- Inflammation causing pains
- Iron deficiency Anemia from bleeding. Massive bleeding may require blood transfusion and urgent hemorrhoidectomy
- Ulceration may lead to secondary infection
- Septic embolism may occur through the portal system to cause liver abscess or pylephlebitis (inflammation of the portal vein) (this is rare)
- Auto- hemorrhoidectomy (obliteration of the hemorrhoids by formation of a fibrous tissue)
How to get rid of hemorrhoids
- Eat food that is rich in dietary fiber such as vegetables to avoid constipation
- Drink enough water
- Always go to the toilet whenever you feel like to pass stool. The more you feel like to defecate and you dont, it makes the stool become compacted and hardened thereby causing constipation which makes hemorrhoids to set in.
- Do not eat heavy meals when you are about to go to sleep
- See your doctor immediately once you suspect you have hemorrhoids; this will enable prompt treatment and prevent it from worsening and becoming complicated.
Treatment of hemorrhoids
- Sitz bath
- Antiseptic creams or ointments
- Use of suppositories
- Surgical treatment
Sudden attacks of hemorrhoids may be relieved by application of antiseptic creams or ointments or use of suppositories. These do not cure the hemorrhoids but provide temporary relief. Warm water with salt added to it known commonly as Sitz bath can be used by sitting in the warm solution.
Surgical treatments for hemorrhoids
There are various methods of surgical procedures that are used for treating hemorrhoids depending on the degree of the hemorrhoids which include:
- Injection Sclerotherapy
- Cryotherapy
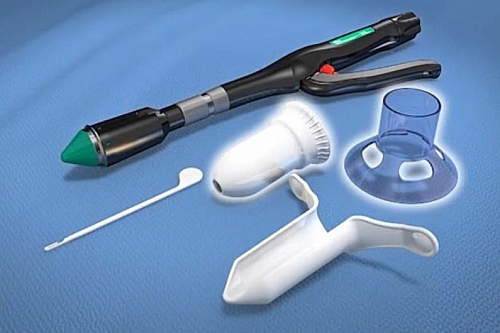
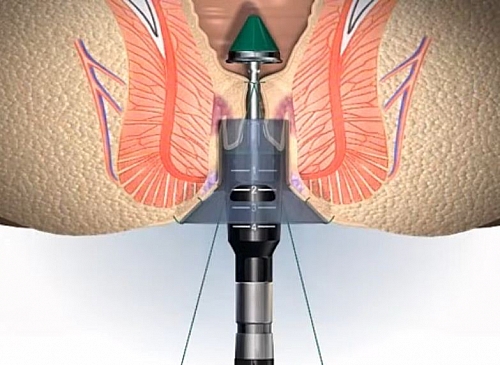
- Rubber Banding Ligation
- Laser or infrared coagulation
- Surgical excision known as hemorrhoidectomy
Injection sclerothrepy
This treatment is suitable for first degree and some second degree hemorrhoids especially when bleeding is the only symptom; it involves the use of a sclerosant agent in the tissue that surrounds the hemorrhoids. 5% phenol in almond oil or arachis oil is mostly used as the sclerosing agent with the phenol serving as an antiseptic agent; the injection is administered using Gabriels syringe (Luer-lock syringe). 5mls of the sclerosing agent is injected into 2 or 3 hemorrhoids and are repeated after every 3 weeks until 3 doses are given. In total, this therapy may last for 9 weeks. This agent causes fibrosis (formation of fibrous scar). Injection is given with the aid of the protoscope mentioned earlier. Injection sclerotherapy has a very high cure rate, with 75 people out of 100 being cured when this method of treatment is applied.
Rubber band ligation
Used for treating 1st and 2nd degree hemorrhoids and has a cure rate of 70%. It involves placing of a rubber band at the base of the hemorrhoids. Not more than 2 hemorrhoids are banded at a time. Minor hemorrhage (bleeding) may occur after 6 or 7 days following banding but if bleeding becomes severe, the patient will have to be admitted in the hospital.
Cryosurgery
This involves the rapid freezing followed by rapid thawing of the hemorrhoids using liquid Nitrogen at temperatures of about -1600C. The procedure is painless but its main challenge is that it causes sloughing-off of the hemorrhoidal tissue with discharge from the anus, few hours after the procedure and may last for about 4 weeks that will require the patient to use surgical pads for 2 or 3 weeks. 2 to 4 pads per day may be needed to pack the anus to help drain the discharge.
Infrared/Laser surgery
This is similar to the cryosurgery but laser light is used to create a burn. It has less side effects and less painful than other procedures.
Hemorrhoidectomy
This is the surgical removal of the hemorrhoids and it is the method of choice for external hemorrhoids or third degree types, however, it comes with its own complications such as anal tags, anal stenosis (reduction in the size of the anal opening), infections and hemorrhage.