Table of Contents
- Ectopic Pregnancy Meaning
- What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
- How common is Ectopic Pregnancy
- Common sites of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Common sites of Ectopic Pregnancy from highest to lowest
- Ectopic Pregnancy Causes (What causes Ectopic Pregnancy)
- Chances of Ectopic Pregnancy (Risk Factors)
- Early Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
- Signs of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
- Ectopic Pregnancy Tests
- Serum b-hCG in the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Ultrasonographyin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Progesterone Levelsin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Culdocentesisin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Curettagein the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Laparoscopyin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasoundin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
- Ectopic Pregnancy Complications
Ectopic Pregnancy Meaning
It is implantation of the fertilized ovum outside the normal uterine cavity. Ectopic Pregnancy is the most common cause of maternal death in the first half of pregnancy.
What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is a type of pregnancy in which the product of conception develops outside the uterine cavity the commonest site being the fallopian tube. It may also occur in rarely in uterine cornu, ovary, cervix, abdominal cavity and broad ligament. In a rare situation, an intrauterine normal pregnancy may co-exist with ectopic pregnancy (in this case, it is referred to as a Heterotopic pregnancy).
How common is Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy occurs in about 1 in 200 pregnancies in the United Kingdom; 1 in 30 in the West Indies and in the United States of America, it is found twice as commonly in the non-white as in the white population. The incidence has been rising slightly, but the death rate of about 1 per 1000 ectopic pregnancies has been falling due to earlier diagnosis and treatment in western societies. In other countries, especially in Africa, the incidence may be as high as 1% because of the higher prevalence of chronic tubal disease.
Common sites of Ectopic Pregnancy
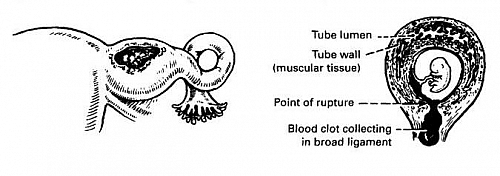
- The commonest site of occurrence of Ectopic Pregnancy is the fallopian tube. About 95% of Ectopic Pregnancies occur in the tubes; when this happen it is called a Tubal Pregnancy.
- Other rare sites or location of Ectopic Pregnancies are the ovaries, a rudimentary horn of a bicornuate uterus , broad ligaments, peritoneum and cervix. These sites together make up 5% of all Ectopic Pregnancies.
Common sites of Ectopic Pregnancy from highest to lowest
- Ampullary region 80%
- Isthmus 12%
- Fimbria 5%
- Cornual/Interstitial 2%
- Abdominal 1.4%
- Cervical 0.2%
- Ovarian 0.2%
Ectopic Pregnancy Causes (What causes Ectopic Pregnancy)
- Infections affecting the reproductive organs: infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), Post-abortal sepsis, puerperal sepsis, and salpingitis.
- Previous history of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Previous history of tubal surgery
- Age of 35 to 44 years: this happens due to loss myoelectrical activity in the fallopian tube.
- Failed Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD)
- Assisted reproductive technology
- Ovulation induction
- Cigarette smoking: this leads to delayed ovulation, altered immunity, altered tubal motility and altered uterine motility.
Chances of Ectopic Pregnancy (Risk Factors)
- Previous pelvic surgery
- Progesterone only pill (POP)
- Depoprovera
- Emergency contraception
- Sterilization
- Early age of intercourse and multiple partners (History of infertility)
- Strenuous physical exercise
- In utero DES exposure
Early Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
The signs and symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy are mainly Amenorrhea, Sudden onset of abdominal pain and bleeding in which an ultrasound scan shows an empty uterine cavity with positive bHCG in serum or urine. These are the early signs and symptoms before complications such as rupture of the ectopic pregnancy occurs.
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
- Cessation of menstruation (Amenorrhea)
- Sudden onset of abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Shoulder tip pain
- Dizziness
- Fainting spells
- Fatigability
Signs of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Pallor
- Abdominal tenderness
- Abdominal distension
Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy involves use of Clinical findings, Laboratory test , Ultrasound and Laparoscopy. Combining these help in making a diagnosis as well as treatment.
Ectopic Pregnancy Tests
Serum b-hCG in the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Urine pregnancy tests are positive in only 50-60% of Ectopic pregnancies. Detection of b -hCG in the serum by ELISA or radioimmunoassay are more sensitive and can detect very early pregnancy about 10 days after fertilization i.e. before the missed period. If the test is negative, normal and abnormal pregnancy including ectopic are excluded. If the test is positive, ultrasonography is indicated.
Doubling time: In normal pregnancy, the b -hCG level is doubling every 48 hours during the first 42 days of gestation. Ectopic pregnancy usually shows less than 66% increase in b -hCG level within 48 hours. Unfortunately, this is not specific to ectopic pregnancy. In 15% of normal pregnancies as well as in abortions there is also slow doubling time. Alpha-hCG subunit level is higher in ectopic pregnancy than normal gestations.
Ultrasonographyin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
In general, a positive b -hCG test with empty uterus by sonar indicates ectopic pregnancy. This is true if the b-hCG is at or above the threshold level in which an intrauterine gestational sac can be detected. This is called discriminatory zone.
Discriminatory hCG zones: Diagnosis of Ectopic pregnancy is made if there is: An empty uterine cavity by abdominal sonography with b -hCG value above 6000 mIU/ml. or An empty uterine cavity by vaginal sonography with b -hCG value above 2000 mIU/ml.
Progesterone Levelsin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Serum progesterone level is lower in ectopic than normal pregnancy and usually less than 15ng/ml. A serum progesterone level of more than 25ng/ml excludes Ectopic Pregnancy.
Culdocentesisin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
If non-clotting blood is aspirated from the Pouch of Douglas through a wide pored needle, intra-peritoneal hemorrhage is diagnosed. But if not, ectopic pregnancy cannot be excluded.
Curettagein the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
If microscopic examination of the products of curettage reveals decidua and chorionic villi, the condition is abortion of intrauterine pregnancy. If it reveals decidua only or Arias Stella reaction in the endometrium as well (cellular atypism, mitotic activity and glandular proliferation), ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed. The drawback is that in complete abortion also decidua only is curetted.
Laparoscopyin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
A good diagnostic aid particularly in disturbed ectopic pregnancy. It is both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasoundin the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Use of Ultrasound in the diagnosis of Ectopic pregnancy makes use of the Kadars Criteria. Vaginal ultrasound scan allows earlier detection of pregnancy and can detect pregnancy 1 week before trans-abdominal ultrasound.
Laparoscopy can assess pelvic structures and also help to outline the exact location of the Ectopic Pregnancy.
Kadars Criteria for Diagnosis Ectopic Pregnancy with Ultrasound
- Ectopic Pregnancy should be suspected if an abdominal ultrasound cannot pick and intrauterine pregnancy when serum bHCG is at least 6000 to 6500 IU/L
- Ectopic Pregnancy should be suspected if trans-vaginal ultrasound cannot pick intrauterine pregnancy when serum bHCG is at least 1000 to 1500 IU/mL
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Ectopic Pregnancy treatment can be done using 3 different types of approaches or a combination of any. These approaches include: Expectant management, Medical or Surgery
Criteria for Expectant Management of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Asymptomatic Ectopic Pregnancy
- No evidence of ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
- Evidence of declining levels of bHCG (<1,500IU/L)
- No evidence of cardiac activity
- If patient is willing to comply with follow-up
- Accept risk of tubal rupture
- If the gestational sac is <3cm in its greatest diameter
Criteria for Medical Management of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hemodynamically stable patient
- No signs or symptoms or active bleeding
- No sign of cardiac activity
- bHCG levels <3,000IU/L
- no contraindications to methotrexate administration
- Ectopic Pregnancy should not exceed 3.5 cm in its greatest diameter
Drugs used in treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Methotrexate
- Mifepristone
- Actinomycin D
- Hyperosmotic Urea
- 23% Potassium Chloride (23% KCL)
- Prostaglandins
- Etopoxide
Use of Methotrexate in treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Commonly used drug is Methotrexate and given as either single dose or multiple dose.
Single dose Methotraxate: given Intramuscularly as 50mg/m2 and no folinic acid rescue. If there is no fall in bHCG even after administration of the single does, it can still be repeated after 7 days.
Multiple dose Methotrexate: this is given as 1mg/kg on alternate days with Folinic acid rescue.
Side effects of Methotrexate in treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Angular stomatitis
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Impaired Liver function tests
- Alopecia
- Neutropenia
Surgical treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Surgical management of Ectopic Pregnancy could be conservative surgery or radical surgery. Conservative Ectopic Pregnancy surgery removes only the Ectopic Pregnancy without the tubes, examples of all conservative surgery includes linear salpingostomy and radical conservative management while the salpingostomy. Radical Ectopic Pregnancy involves removal of some parts of either the uterus or the tubes.
Ectopic Pregnancy Surgery
- Linear Salpingostomy: in this surgery, the antimesenteric border of the tube is incised and the product of conception is expelled. The incision is made to heal by secondary intention
- Salpingotomy: in this type of Ectopic Pregnancy, the incision site is closed by fine suture.
- Salpingectomy: this could be Partial salpingectomy (in which part of the tube is left) and Total salpingectomy (whereby the whole tube is removed)
- Cornua resection and re-implantation
Ectopic Pregnancy Complications
- Ectopic Pregnancy Pain: Ectopic Pregnancy pain location is often unilateral due to spasm of the tubal muscle. There may be referred shoulder pain via the phrenic nerve from blood in the abdominal cavity.
- Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy: This presents as an acute abdominal emergency with collapse, severe abdominal pain, pallor, rapid pulse and hypotension; blood may track up under the diaphragm giving shoulder pain; the abdomen is slightly distended, tender and rigid; On vaginal examination, the uterus is soft and may be enlarged but is very tender; a tender tubal mass may not be palpated because of the extreme tenderness and guarding
- Ectopic Pregnancy Bleeding: when a pregnancy implants in the fallopian tube, the uterine endometrium is still converted into decidua. When the embryo dies, the decidua in the uterus separates. The bleeding is usually scanty, less than a normal period and dark brown in color.