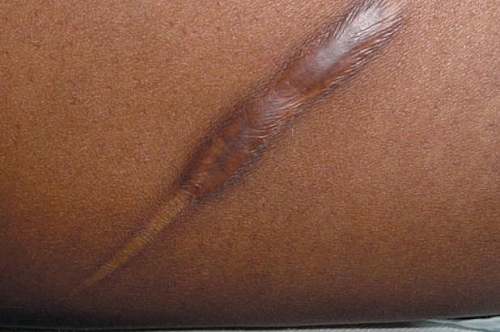
The differences between Hypertrophic scar and Keloid can distinguished by their location, borders (edge), their course, age at which the scar is common, the gender commonly affected, the race mostly affected and the genetic makeup of the individual.
Table of Contents
Differences between Keloid and Hypertrophic scar
- Keloid mostly occur at the ear, head, neck, shoulders and the chest (around the sternum) whereas hypertrophic scar can occur anyway
- A keloid can grow to extend beyond the normal boundary, encroaching to normal skin tissue whereas hypertrophic scar rarely outgrow its boundaries
- Few weeks after an injury, a keloid starts growing and the growth becomes continuous but the growth of hypertrophic scar after injury normally subsides with time
- Keloids commonly occur between the ages of 10 to 30 years while hypertrophic scar occurs at any age whether a baby or an elderly individual
- Keloids occur more in Africans than in Caucasians but there is no racial preference with hypertrophic scar. It is 15 times more commoner in highly pigmented people
- There is family predisposition of keloid but less in hypertrophic scar
- Pregnancy and puberty cause increase in size of keloid
- Claw like growth or crab like growth is seen with keloids but linear growth is seen in hypertrophic scar
- Hypertrophic scar tends to regress after 1 year
- Keloids are difficult to treat; earlobes keloids are the only ones that are easier to treat by excision
- Keloid may become malignant (change into cancer)
- Keloids have high rates of recurrence
Comparison between hypertrophic scar vs Keloids
- Both occur following an injury
- All cause formation of scar tissue
- Affects both males and females alike but there is higher incidence in young females which is due to earlobe piercing.
- There could be associated pain or itching in both hypertrophic scar and keloid
- Complications could arise in both, giving rise to an ulcer (wound) or discharge. Contractures may occur if the scar tissue is formed around the joints.
Hypertrophic scar and keloids can cause discomfort especially when they cause itching and pain apart from also affecting the look of an individual. Early treatment helps in the prognosis even though keloids may recur.
Keloid Treatment
- Use of radiotherapy
- Use of intralesional triamcenelone injection (this is a steroid)
- Surgical Excision
- A combination of any of the above can be done
Hypertrophic scar Treatment
Treatment for Hypertrophic scar basically is by use of compression stockings as it regresses after a year.