Table of Contents
- What is biology?
- Origin of Biology
- Modern Biology and its basic principles
- Branches of Biology
- Some Careers and Jobs in Biology
- Importance of Biology
- FAQ
- Is biology a hard subject or course?
- Is biology a major in medicine?
- How much is the salary of a biologist?
- What are the highest paying jobs in biology?
- How biology is linked with other sciences?
- How biology is an important subject?
- Why biology is important for a student?
- What are the most important things you learn in biology?
- What are the 3 types of biology?
- What are the 3 main branches of biology?
- What are the 4 types of biology?
- What is biology study?
- What is a cell?
- What does a biologist do?
- What are living things called in Biology?
What is biology?
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is the study of the origin, structure, function, growth, evolution, and distribution of a living organisms. Biology is a combination of the Greek words “bios” meaning life and “logos” which means knowledge or study. Biology is a very broad topic that includes many fields of study. The largest fields are cell biology, microbiology, ecology, zoology, and botany.
Origin of Biology
Meanwhile, no one can really put an exact time stamp on when or where the study of life forms began, but history has shown that from the stone age, humans had the knowledge to differentiate between edible and poisonous plants, they knew which animals were wild and which they could domesticate and train.
Therefore, it is said that it dates back before humans had the knowledge of writing and keeping records.
During 1800BCE a record of the cultivation of date palm was kept by the Assyrians and Babylonians. Then further down the line, during the Greek civilization, indeed many pools of knowledge were open and many theories in science started to emanate, and earlier in the 4th century BCE, the rise of Aristotle as the father of biology came into existence as he tried to classify animals and started many biological investigations in the aspect of reproduction and heredity.
Modern Biology and its basic principles
There are 4 unifying principles governing modern biology namely;
- Cell theory
- Gene theory
- Homeostasis
- Evolution
These principles are going to be discussed subsequently.
Cell theory
The characteristics of cell theory are;
- all living things are made up of fundamental basic units called cells
- one or more cell makes up and organism
- Through cellular division, more cells are formed. it can equally be said as other cells are formed from preexisting cells
- all cells contain genetic information and pass it down to daughter cells during cell division in the cell cycle
- metabolism and biochemistry of the cell also known as the energy flow occur within the cell
- the chemical composition is virtually the same in all cells
Cell Structure
In cell theory, Biologists study the structure of cells. Understanding how cells fit and function together is extremely important because they are the basic unit of all life in biology. 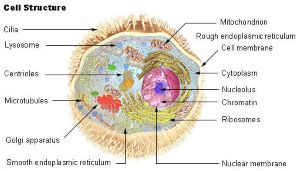
Examples of topics in cell structure include organelles in the cytosol or cytoplasm such as; centrosomes, cytoskeleton, vacuoles, cell wall, enzymes, and the golgi complex.
Cell structure can be broken down further into the categories of unicellular organisms such as Protista, and multicellular organisms. This is also often represented by eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Biologists also look at various cell functions including diffusion, active transport, meiosis, and mitosis.
Gene Theory
In the middle of the 19th century, Gregory Mendel, who is known as the father of genetics proposed that genes found in living organisms are the basic unit that carries the characteristics or traits of the organism.
These genes are then passed down from one generation to the next. This theory gave way to modern topics of study including genotype, plasmids, and binary fission. These topics are still essential and are being studied by prospective geneticists at various educational levels, from those still pursuing their undergraduate degrees to those who are furthering their education by studying for an on-campus or online masters in genetics.
Homeostasis
The idea was first coined during the 19th century by the French physiologist that goes by the name Claude Bernard, and he postulated that living organisms as different as they maybe have one thing in common, which is to maintain their condition to survive. In essence, it is the ability of an organism to maintain its internal environment.
Evolution
And in his theory, Charles Darwin postulated the process of natural selection as the basis of the evolution of living things. He hypothesized that living organisms can change through mutation of genes, to possess genes that have a far greater chance of adapting to their changing environment. And these new genes are therefore transferred through the genetic makeup of the parent to their offspring.
The subject topic cannot be evenly dissected without discussing some core topics namely;
- Branch of biology
- Major career and job options in biology
- Importance of biology
Branches of Biology
The study of life is diverse, therefore it is said that it has many branches and sub-branches or sub-divisions. Hence, a comprehensive approach is taken to understand the divisions in this study afterward. Needless to say, there are 5 main divisions of biology, namely; Botany, Zoology, Microbiology, Ecology, and Human Ecology.
Therefore, in each of these five divisions, there are sub-divisions, which are covered to some extent. Because of the growing changes in every field and the formation of newer fields in biology, the whole branch of biology cannot be stated. Thus, a summary of each major division and sub-division will be analyzed subsequently.
Botany
The word is coined from the Greek word botane meaning “plants, pastures, and grasses”. Therefore, it is the study of the living organisms from the kingdom Plantae. Which is arguably known as plants. 
One who pursues a career in this field is also known as a Botanist. Also the Greek scholar Theophrastus is known as the father of Botany. As he was the first to perform an in-depth analysis of the plant kingdom in the 4th century BC. He in fact opened the flood gates and led the way to modern scientific discoveries. Hence, paving the way for more sub-disciplines in the field.
There are 3 subcategories used as a criterion in botany. Biological research, type of plants, and applied plant sciences.
Biological research
Biological research in Botany includes the following categories:
- cytology (study of plant cells)
- Plant anatomy (study of plant structure)
- plant genetics (study of plant genes)
- paleobotany (study of plant fossil)
Cytology
Cytology is the study of plant cells. This includes the anatomy, processes, and functions of plant cells.
Cytologists spend a lot of time looking at plant cell structure. Examples of topics in plant cell structure include; stomata, thylakoids, chlorophyll, plastids, guard cells, and chloroplasts.
Plant Anatomy
Botanists also study plant structure and processes such as the transfer of energy via ATP during

photosynthesis. Other important processes in botany include osmosis, endocytosis, exocytosis, plasmolysis, effects of turgor pressure, and transpiration.
Plant anatomy involves looking at the relationship between a plant’s structure and the independent functions each part has. For example the function of roots, the nutrient transport system between phloem and xylem, asexual reproduction in plants, pollination, and tropism.
Type of plant category
they are namely;
- Mycology (fungi study)
- Phycology (algae study)
- Pteridology (ferns study)
- Lichenology (both fungi and algae study)
Applied plant science category
we have the following sub-discipline namely;
- Plant pathology (plant disease study)
- Agronomy (crop and science study)
- Horticulture (flowering and ornamental plant study)
- Plant breeding
- Forestry
On the whole, one can have a successful career in botany when they choose to study any of the above mention careers, not only that, they need to Major in biology. Hence meaning that they must have a good understanding of the basic fundamentals of biological science.
Zoology
This is the study of the kingdom Animalia. It deals with the scientific study that involves the animal kingdom. Studies like for example, Animal classification, embryo development, Ecological distribution of animals, evolution, and behavior.
The word is derived from the Greek words ZŌION meaning “animal” and logos meaning “study of”. Aristotle the Greek scholar and Charles Darwin were the pioneers in this field and they paved the way for modern zoological studies and findings. Thus the theory of evolution by natural selection postulated by Charles Darwin gave way for animal taxonomy, alongside the evolutionary relationships between animals and the genetic information in animals.
Zoology is broken into many sub-division based on the type of animal study, and biological studies.
Biological Study
The branches under this criteria are as follows;
Zoography, Ethology, Behavioral ecology, Animal Physiology, and Comparative Anatomy.
Zoography
This is the study of animals and their habitat. It deals with the spatial distribution of these animals in different geographical locations and their effects on the ecosystem they belong to.
For example a zoologist might study tropical rainforest animals or animals in the arctic.
Ethology
Furthermore, the works of Darwin led the way in this field as it is the study of animal behavior in their natural environment. Such study involves animal learning, sexuality, communication, and cognition.
Behavioral Ecology
In addition, this field stems out from ethology as it also deals with the study of animal behavior. It deals directly with the adverse effects of the environment on animal behavior and evolution. From the thesis of survival of the fittest, it is said that the animals with the best traits that allow adaptation will thrive more than those without such traits. Behavioral Ecologists study animal competition.
Comparative Anatomy
As the name implies, it is the study of the differences and similarities in animal anatomical structures. It is also a field that is used in paleontology and in the evolutionary trend of animals.
Animal Physiology
Again, this is the study of the processes that occur in the body of an animal, which allows it to maintain or keep its internal environment. The process of maintaining the internal environment in equilibrium is known as Homeostasis.
This field involves the study of blood flow and pressure, temperature regulation in endotherms and ectotherms, and the release of hormones by the body at certain times in the body.
Types of Animal Branches
This category is based on the different classifications of animals that can be studied and specialization can be gained. These branches are named below;
- Mammalogy (study of mammals) also has a sub-division known as Primatology which is the study of primates as the name implies.
- Ornithology (known as the study of birds)
- Entomology (which is insect study and it has some sub-category like myrmecology and coleopterology)
- Ichthyology (fish study)
- Herpetology (Reptile and amphibian study)
In a word, a career can actually be earned in zoology. When the passion and love for animals are developed. Thus, they can work in zoos as curators, in laboratories, or be out there in the field as wildlife rehabilitators fighting for endangered species through the collection of data. Finally, in other to develop or build a successful career, biology is a prerequisite before eventually branching into zoology.
Microbiology
From the word “micro” meaning small, it can be said that microbiology is the study of living things that cannot be seen with the naked eyes. Thus, it is a deep dive into the world of the minute organisms which includes but is not limited to bacteria and fungi. During, the 17th century, Anton Leeuwenhoek used a primitive microscope to observe bacteria in water, which was published. Indeed, this publication revolutionized the field, and coupled with the further invention of the compound microscope, microbes truly be seen and described in detail. Hence, this field can only get bigger and better with the advancement in technology.
The field of microbiology can be broken or classified based on two criteria: taxonomy and types of research.
Taxonomy
- Virology (virus study)
- Mycology (fungi study)
- Bacteriology (bacteria study)
- Parasitology (parasite study as most are microbial in nature)
- Immunology (immune system study with relation to pathogen and their host)
- protozoology (single-celled organism study like protozoa and amoeba)
- Phycology (Algae study)
- Nematology (Nematode study)
Types of research
Microbial researches are conducted as pure or applied. and in each of this subcategory, the branches are namely;
Pure Research:
- Microbial Ecology
- Microbial Genetics
- Cellular Biology
- Microbial Physiology
- Systems microbiology
- Astromicrobiogy
- Evolutionary microbiology
Applied Research:
- Food microbiology
- Pharmaceutical microbiology
- Microbial Biotechnology
- Medical microbiology
- Agricultural microbiology
In microbiology specializations in food, environmental, medical, or pharmaceutical microbiology can be obtained. Examples of topics in microbiology include gram positive bacteria, gram negative bacteria, euglena, parasites,
Ecology
Ecology is a branch of biology that deals with the interactions of living things amongst themselves and with their environment. Ecology includes the study of humans and their biomes known as Human Ecology and the study of the environmental factors affecting the evolution of animals known as environmental biology.
The branches of ecology are as follows; molecular ecology, ecosystem ecology, organizational ecology, population ecology, and community ecology.
Molecular Ecology
The study of this field deals with the production of protein by an organism, how this protein affects the organism, and environment, and how the environment affects the organism’s ability to produce more protein. So the interaction between all these factors happens at a molecular level as shown in the diagram below;

Organismal or species ecology
This is the study of the interactions between an individual organism with other organisms and the environment. A clear example of such is the predator-prey relationship. In this kind of interaction, ecologist studies the success and failures of the predator and prey.
Because of the billions of organisms that have ever graced this planet, it is therefore classified as a broad field. There are many interactions an organism can have during its life cycle. For example, an ecologist might specialize in the study of their behaviors, the way they obtain nutrients, their chemical decomposition reactions.
Population ecology
This is the study of the interactions of the same groups of organisms known as population. The study is more on how they affect each species in competitions known as intra-specific competition. Some species compete amongst themselves for space and food, while other species organize themselves and work together for the growth of the population.
In summary, it is concerned about the complex relationship or interaction a population and its relationship with other populations and the environment.
Community Ecology
When populations of different organisms live together in a particular geographical location it is called a community. Therefore, this is the study of the complex relations of each species population to the other known as interspecific competition.
This competition often presents itself in within the trophic levels of the food web. The represents the relationship between heterotrophs and autotrophs.
The food web is further broken down into the levels of primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. These are often represented by producers, herbivores, omnivores, and carnivores.
Such competition is a result of either favorable or unfavorable environmental parameters or factors. For example desert plants or desert animals have specific environmental adaptations to help them survive the harsh climate.
Ecosystem Ecology
An ecosystem is a combination of many interrelated biological communities. Therefore, it is the study of the complex relationships or interactions between an ecosystem and the abiotic environmental factors.

This includes various biogeochemical cycles such as the water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and nutrient cycle.
As an ecologist, the opportunities for work are enormous, as there are many fields and specializations. Topics within ecosystem ecology include the study of air pollution, water pollution, and symbiotic or mutualistic relationships such as commensalism.
The sum of all ecosystems across the globe make up what is known as the biosphere. This can be broken down into ecosystems by geographical area known as biomes. Examples include Chaparral Biomes, Desert Biomes, Marine Biomes, and Tundra Biomes.
Human Biology
This is an academic branch of biology that deals with the role of humans on the earth. It focuses more on how we got here, how we have adapted and how we have evolved through the years (genetic modification, anatomic, physiological, and ecological evolution), and how we function. It also deals with how we affect nature and what role the environment plays in our distribution.
Some Careers and Jobs in Biology
Some Career option and branches |
Brief Description |
Aerobiologist/ Aerobiology |
This involves studying organic particles found in the atmosphere |
Astrobiologist/ AstroBiology |
This is mainly concerned with how future life will evolve and distribute in the universe |
Biomedical Research |
A study on health and diseases |
Biotechnologist/ Biotechnology |
The study of how to manipulate living matter (gene modification and synthetic biology) |
Biochemist/ Biochemistry |
This involves the study of all chemical reaction at the cellular level, that is necessary for an organism to exist and function |
Bioinformatics |
This is the study of the collection and storage of genomes along with other biological data through the use of information technology |
Biophysicist/ Biophysics |
This is the use of natural physical theories in the study of biological processes |
Synthetic biology |
This is the study of the construction of biological functions that are not found in nature, by blending knowledge from biology and engineering |
Developmental biologist/ Developmental biology |
This deals with the study of the formation and development of an organism from a zygote to its evolution as an adult. This also has a sub-discipline of embryology, evolutionary developmental biology, gerontology, and teratology |
Nanobiologist/ Nanobiology |
This is concerned with the study of a living organism and its parts on a nanoscale level, and the use of nanotechnology in biological researches |
Molecular Biologist/Molecular Biology |
This is a study that has to do with understanding the molecular structure of an organism |
Molecular Genetics |
This is the study of trait variation and its expression in an organism through the different genetic structure found in its DNA |
Importance of Biology
Its importance cannot be measured, as it is involved in our daily lives. Some notable importance will be listed and hopefully broken down. But there are numerous importances that are so small that occur in our everyday activities. Some key importance’s are as follows;
Aid in our quest to understand nature
There are times when the earth could not be understood, how things came into existence, and how they evolve. Hence, since the conception of curious men trying to know how the earth functions, more knowledge has flooded the earth and the appreciation of nature has grown. Truly, we can now comprehend the nature of heredity, carbon cycle, plant and animal development to mention a few.
Improves the quality of life
In addition, looking at the rate at which science is growing, humans can now plant crops that will germinate and produce more seeds. In fact, this great improvement in botany has helped us to feed the ever-growing population and to improve our lives. Hence, it is achieved because farmers now know what species of crops to plant, how to grow them, and what to do when competition arises in the form of weeds. Likewise, in animal production.
Helps us to understand medicine
Also, with the advancements in aspects of botany, plants, chemical properties are synthesized to produce more drugs that come to our aid when we are sick. Furthermore, the understanding of microbes that causes certain diseases is well documented, hence, an understanding of how an organism reacts with its natural environment can lead to a breakthrough in medical research.
Helps us understand our bodies
Again, we can now boast of a greater understanding of how our bodies function. Truly, with such knowledge, we can treat it better and optimize its function. In fact, we now have a comprehensive understanding of the developmental stages in humans and what to look out for when we notice any red flags in these stages.
In brief, the study of biology can only get better with advancements in technology. Some centuries ago we could not view a cell, but currently, we can view one with colors, how cool is that! Let’s study this field, in other to help nature provide us with better functions. And to uncover much knowledge that can lead to better living.
FAQ
Is biology a hard subject or course?
Just like every other subject, a person needs to develop passion and love towards the study of biology, otherwise, it becomes a hard subject. Furthermore, knowing the vast nature of this field, it is best to brace up for the joy ride ahead.
Is biology a major in medicine?
One who majors in biology can switch towards the field of medicine. This is because the fundamental knowledge of life has been obtained and a smooth transition can take place.
How much is the salary of a biologist?
Depending on your qualifications, because the average salary for a fresh graduate, is $40,688 and that of an experienced biologist is $62,067 per annum.
What are the highest paying jobs in biology?
Some of the jobs that can pay well in this field are as follows;
- Respiratory therapist
- Genetic counselor
- Microbiologist
- Pharmaceutical sales representative
- Environmental scientist
- Health communications specialist
How biology is linked with other sciences?
Biology is linked with other sciences because it has many related branches including ecology, microbiology, cell biology, and botany.
How biology is an important subject?
Biology is an important subject because it allows us to understand how life works at a cellular level. It helps us understand how organisms and their environments interact and further develop technology according to this.
Why biology is important for a student?
If you love to learn about living things and how they relate, studying biology might be the right fit for you. A biology major gives you an in-depth understanding of the natural world. It also helps you learn how to conduct research, problem solve, organize, and think critically.
What are the most important things you learn in biology?
Major biological concepts for student focus include homeostasis, energy transfer and use, the relationship between structure and function, and change over time. Additionally, students’ experience in biology supports their developing environmental literacy.
What are the 3 types of biology?
3 types of biology are microbiology, ecology, and botany.
What are the 3 main branches of biology?
The 3 main branches of biology are medical science, zoology, and botany.
What are the 4 types of biology?
The 4 types of biology in modern science are cell theory, gene theory, homeostasis, and evolution.
What is biology study?
Biology is a natural science discipline that studies living things. It is a very large and broad field due to the wide variety of life found on Earth, so individual biologists normally focus on specific fields. These fields are either categorized by the scale of life or by the types of organisms studied.
What is a cell?
In biology, a cell is the smallest unit that can live on its own and that makes up all living organisms and the tissues of the body. A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell.
What does a biologist do?
Biologists study humans, plants, animals, and the environments in which they live. They may conduct their studies–human medical research, plant research, animal research, environmental system research–at the cellular level or the ecosystem level or anywhere in between.
What are living things called in Biology?
Living things in Biology are called organisms. An organism is any individual living thing. It is easy to recognize a living thing, but not so easy to define it. Animals and plants are organisms, obviously. Organisms are a biotic, or living, part of the environment.
