Kidd Blood Group History
The Kidd blood group system was discovered in 1951 by Allen and named after Mrs. Kidd, the woman whose serum was found to contain the antibody of this type of blood group while the antigen of the blood group was named Jkafor the initials of the woman’s child whose name was John Kidd, the child was affected by Hemolytic disease of the newborn due to the reaction of the antibodies against the antigens leading to the discovery of this type of blood group system. Anti-Jkb was found in 1953 in the serum of a woman who had a transfusion reaction. This is because Antibodies to the Kidd blood group system are most commonly associated with about one-third of all delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions, which may be severe.
Table of Contents
Kidd Blood Group System
The Kidd blood group system has three antigens: Jka, Jkb and Jk3 which are encoded by a gene known as HUT11 (also known as SLC14A1 gene which stands for Solute Carrier family 14, member 1) located on chromosome 18. The Kidd protein is also a urea transporter, therefore Jk-null individuals have reduced capacity to concentrate their urine and their RBCs are more resistant to lysis by 2M urea, but they display no other abnormalities.
Kidd Blood Group Antigens
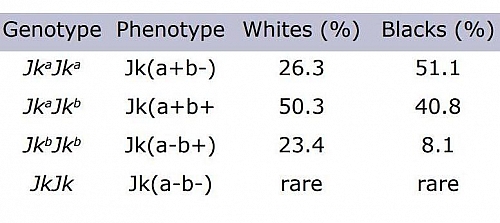
The two antigens Jka and Jkb result from the substitution of a single amino acid that then leads to three common phenotypes: Jk(a+b-), Jk(a-b+), and Jk(a+b+); The final phenotype, Jk(a-b-) is also called the null phenotype but this is rare in whites and African Americans, but is found with increased frequency in Asian and polynesian individuals. The null phenotype arises from either a silent allele or inheritance of a dominant inhibitor gene known as In(Jk).
Kidd Blood Group Antibodies
Antibodies to the Kidd blood group system are not very common but often found in serum that contains other antibodies, and because their titer often falls short of the limit of detection, these kidd antibodies often react weakly and may even become undetectable during storage, and they may react with only homozygous cells (show dosage). Anti-Kidd antibodies can be difficult to identify.
Kidd Blood Group Frequency
The antigens Jka and Jkb are found at relatively the same frequencies in the white populations but differ in other ethnic groups such as blacks and Asians
Kidd Blood Group Phenotype
Kidd antigens can be detected in pregnancy at 11 weeks gestation, and are well developed at birth. These antigens are also found on endothelial cells of vasa recta of human kidney medulla.
Clinical Significance of Kidd Blood Group
For the reason that the Kidd antibodies are difficult to detect these antibodies are responsible for about one-third of all severe delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions. The Kidd antibodies are mainly IgG type of antibodies, but can partially be IgM.
The Kidd antibodies rarely cause Hemolytic disease of the fetus and new born and even when it occurs, it is not severe. Anti-Jk3 antibodies (also known as anti-Jkab ) can be produced by Jk(a-b-) individuals.