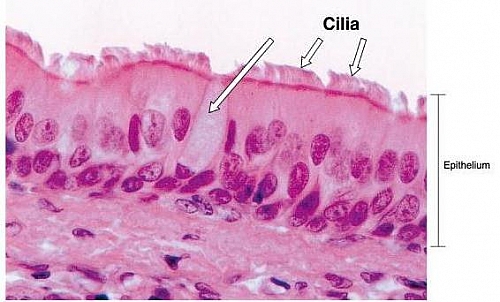
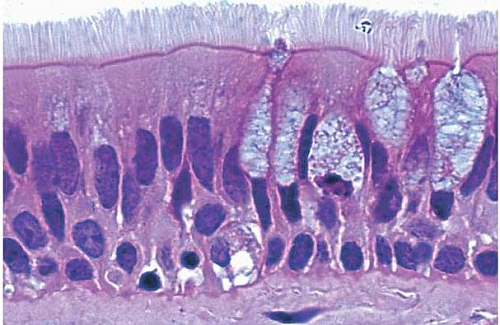
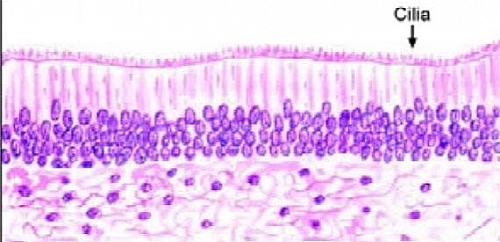
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium is a type of a columnar epithelium which is actually single layered epithelium but may appear as a stratified epithelium hence the name: Pseudo- stratified epithelium (it is not a true stratified epithelium). This type of epithelium when viewed with a microscope will show the nuclei to lie in various layers even though all cells are attached to the basal lamina but some do not reach the surface. The best example of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial tissue is the ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the respiratory tract.
Table of Contents
Histological Structure Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium is a single layer of ciliated, irregularly shaped cells containing many goblet cells. In usual slides the boundaries between epithelial cells are often not clearly seen but because of the shape and spacing of the nuclei, the epithelium can be identified. The Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium lining the ductus epididymis and certain other parts of the male reproductive tract does not have cilia or goblet cells.
In the usual columnar epithelium the nuclei lie in a row, towards the bases of the cells; but that of pseudostratified columnar epithelium appear to be arranged in two or more layers giving the impression that the epithelium is more than one cell thick but it is not the reason for this is that some cells are broader near the base while others are broader near the apex and the nuclei lie in the broader part of each cell, thereby making them not to lie at the same level and appears stratified falsely.
Location of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- Ciliated Pseudostratified columnar epithelium lines the Bronchi
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is found in some parts of the auditory tube
- It is also found in the ductus deferens
- It also lines the membranous and penile parts of the male urethra
- A ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium is seen in the trachea
- They are also found lining tubular glands of the endometrium in females
Functions of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium helps to protect the airways from toxic substances
- The goblet cells in this type of epithelium helps in secretion that keeps the airway moist
- The ciliary action of the cilia on the Pseudostratified columnar epithelium of the airway helps to clear particles as well as excess mucus from the airway.
Medical importance of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Habitual smokers often have prolonged inflammation of the bronchi called chronic bronchitis which increases the number of goblet cells in the lining of airways leading to excessive mucus production in areas where the ciliated cells of the pseudostratified columnar epithelium are so few; this causes obstruction of the airways by the secreted mucus. The prolonged smoking can also cause the ciliated pseudostratified epithelium lining the bronchi of smokers to change into stratified squamous epithelium by a process known as metaplasia and a this process is often a preceding factor that leads to cancer.