Copper T Contraceptive device is a form of Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD) or IUD. It is one of the methods used for Family planning this means Copper T prevents pregnancy. It has its benefits and side effects.
Table of Contents
- What is Copper T?
- How Copper T Works
- Copper T types
- Copper T Images
- How to use Copper T
- Copper T Insertion (Procedure on How to insert Copper T)
- Copper T Removal
- Copper T Contraindications (When not to use Copper T)
- Is Copper T good or Bad?
- Copper T Benefits (Copper T Advantages)
- Copper T Side Effects (Copper T Disadvantages)
- Copper T Complications
- Copper T Cost and Price
What is Copper T?
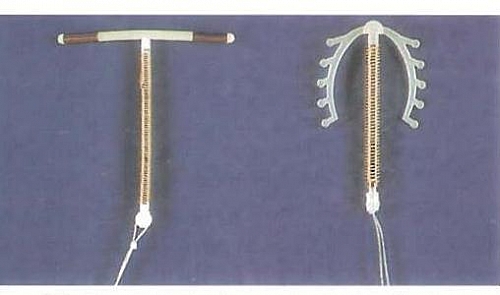
Copper T is a small plastic carrier that has the shape of a T or similar design. The vertical stem of this device is wound some copper wire and the transverse arms may have copper bands. Copper T is sufficiently flexible to be drawn into an introducer for insertion into the uterine cavity. Copper T is renewed every 3 to 5 years because of the gradual absorption of the copper (depending on the type). The copper IUDs are very effective and licensed to last 3-10 years: Copper T 380A has a first year failure rate of 0 to 4 per 100 women and a 5 years failure rate of 1.3 per 100 women.
How Copper T Works
Copper T prevents fertilization and implantation because Copper is toxic to both the ovum and the sperm and also causes an inflammatory reaction in the endometrium. Copper inhibits sperm mobility and activation of acrosome reaction (Copper IUD). The length of time that Copper T can last depends on the type of Copper device.
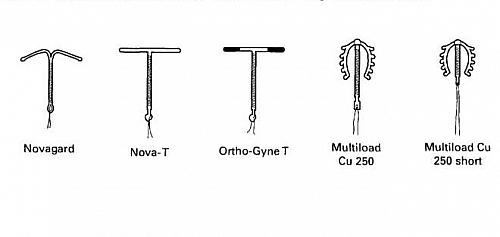
Copper T types
- The Nova T and the Nova Gard both contain silver and copper this has a failure rate of 1- 2 per 100 woman- years
- A Multiload Copper (Cu 250) is licensed for 3 years
- Multiload Copper (Cu 375) this is licensed for 5 years with failure rate of 0.5 per 100 woman-years
- Gynae T 380 slimline this is licensed for 8 years with failure rate as low as 0.5 per 100 woman-years
Copper T Images
How to use Copper T
- The cervix is exposed, swabbed and grasped with tenaculum forceps
- The introducer is inserted and the IUCD expelled into the cavity
- The thread is then cut, leaving about 2 inches in the vagina
- With very nervous women some sedation or even an anesthetic may be required
Copper T can be inserted at any time during the menstrual cycle so far it has been established that the woman is not pregnant or immediately after spontaneous or therapeutic abortion although expulsion rates may be higher in second trimester abortions. Even though Copper T can be inserted immediately postpartum or prior to discharge after 48 hours of delivery, doing so may lead to expulsion of the device as the expulsion rates are higher at this time; because of this, it is recommended that Copper T be inserted at 6 weeks postpartum.
What to do before Copper T insertion
- Note the last menstrual period (LMP), previous medical history and sexually transmitted disease (STD) screening
- Patient should be informed on the efficacy, mechanism of action, possible side effects and risks of Copper T, similar to jadelle impalnts
- Do a pelvic examination to rule out uterine abnormality
Precautions before Copper T insertion
- Copper T insertion should only be done starting from the last day of menstrual flow to day 19 of the menstrual cycle.
- Copper T removal should be preceded by either 7 days of abstinence from sexual intercourse or other contraceptive precautions should be done.
- Ideally, devices should not be removed after day 19 of a 28-day cycle
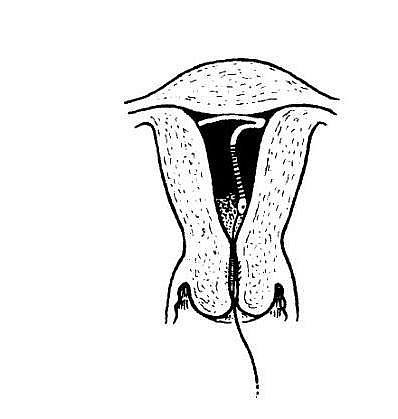
Copper T Insertion (Procedure on How to insert Copper T)
- Copper T insertion is easier when a woman had previously had vaginal delivery; however, Copper T Coil insertion can also be achieved in nulliparous women. In order to reduce the risk of uterine perforation, the woman should be examined vaginally to assess the size and direction of the uterus.
- The introducer is then inserted into the uterus until it reaches the fundus
- The surrounding introducer is drawn back holding the rod in place so that the device has now opened out in the uterine cavity.
- The rod and introducer is now removed carefully and the threads are trimmed to about 4 cm
A local anesthetic and a tenaculum forceps can be useful and occasionally some sedation or even a general anesthetic may be required to insert a coil. Follow-up after Copper T insertion is important after 36 weeks to assess and ensure there is no infection because this is the period of highest risk of infection following Copper T insertion.
Copper T Removal
Unless pregnancy is desired, Copper T removal should only be undertaken in the late luteal phase or in the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle. In menopausal women, it should be left in for one year after the last menstrual period. If Copper T threads are not visible or snap during removal it may be possible to remove it with a specially designed hook or a pair of artery forceps.
Copper T Contraindications (When not to use Copper T)
- History of previous Ectopic pregnancy
- Subfertility
- Congenital malformation of the uterus
- Genital tract malignancy
- Suspicion of pregnancy
- Unexplained uterine bleeding.
- Wilson’s disease
- Copper allergy
- Immunosuppression such as HIV
- Where infection would be of grave concern such as in bacterial endocarditis, previous tubal pregnancy and the presence of prosthetic heart valves
- Uterine Fibroids are not a contraindication to Copper T insertion unless the uterine cavity is distorted
- Previous cervical surgery resulting in stenosis may make insertion difficult and the coil should not be fitted during active pelvic infection
Is Copper T good or Bad?
Copper T is good only when there are no contraindications to its use but becomes bad when it is still used even with contraindications. Copper T is a very good and effective method of contraception and can be use for Family planning by couples. It is very useful when long term contraception is needed without worrying over compliance such as the use of pills.
Copper T Benefits (Copper T Advantages)
- Convenient method of contraception with very low failure rate
- Method not related to intercourse, permitting spontaneity of sexual activity
- Rapid return of fertility on removal of Copper T
- Cost effective
- Ideal method for women who cannot remember to use pills every day
Copper T Side Effects (Copper T Disadvantages)
- Heavy bleeding after Copper T insertion could occur (Menorrhagia)
- Painful menstrual periods (Dysmenorrhea) may occur too
- Expulsion of Copper T this occurs most often in the first few weeks after insertion
- Perforation mostly occurs with inexperienced fitters or when the uterus is retroverted
- Pain this can be prevented by use of Lidocaine (lignocaine) gel which can be inserted intra-cervically; Paracervical block can also be done prior to insertion of copper T. Other methods of reducing pain during Copper T insertion include Oral analgesia (NSAIDs) or Voltarol suppositories, given prior to fitting. Copper T insertion is not painful only when measures are taken to reduce or prevent pain as mentioned.
- Prolonged vasovagal bradycardia
- Bronchospasm
- Small risk of infection: there is increased risk of pelvic infection in the first few weeks following insertion of Copper T.
Copper T Complications
Increased menstrual blood loss
Heavy bleeding (Menorrhagia) following Copper T insertion may be due to the increased fibrinolytic activity that forms around the device but this can be minimized by the use of anti-fibrinolytic agents such as tranexamic acid. Some anti-prostaglandin agents like Mefenamic acid or Diclofenac are also effective in preventing excessive bleeding.
Pelvic Infection
Copper T increases the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), especially during the first months after insertion, hence the reason why women with active pelvic infection should not have a Copper T coil inserted. Women with an existing coil in place may be given antibiotic treatment with the coil left in place; but when infection becomes severe or persistent, the device should be removed.
Pregnancy and Failure of Copper T
The chances of being pregnant with Copper T in situ are very low and this occurs mostly in the first 2 years; because of the low risk of being pregnant when using Copper T, the risk of ectopic pregnancy is also lower compared to those who do not use Copper T; but if there is failure of Copper T to stop pregnancy and it happens that the woman becomes pregnant, her chances of having an ectopic pregnancy will be high.
Expulsion of Copper T IUD
This may occur in 510% of cases and usually happen within the first 6 months after insertion. It is recommended that a speculum examination be performed at 6 weeks after Copper T coil insertion to check that the threads are visible. If the threads are not visible, an ultrasound scan should be performed to check for the presence of an intrauterine coil.
Translocation of Copper T IUD
It is possible for copper T to pass through the uterine wall into the peritoneal cavity or the broad ligament especially with faulty insertion. An intrauterine coil is usually identified on scan but an extra-uterine coil can be very difficult to visualize using the ultrasound. When this occurs, a laparoscopy and possible laparotomy, may be needed to locate it.
Copper T Cost and Price
Copper T is not costly and is very cost effective.