Cysticercosis is a disease caused by the larvae of parasitic tapeworm called Taenia solium (Pork Tapeworm) that leads to the formation of cyst in the organ it affects: when it affects the brain, it is called Neurocysticercosis or Cerebral cysticercosis and when it affects the eyes it is called Ocular Cysticercosis. Adult Taenia solium infection together with the one caused by Taenia saginata (Beef tapeworm) are known as Taeniasis or Taeniosis; Taeniasis therefore is any infection caused by adult tapeworms that mainly affects the intestines. Therefore, the adult Taenia solium causes Taeniasis while the larvae (known as cysticercus cellulosae or simply cysticercus) cause cysticercosis.
Table of Contents
Cysticercosis Epidemiology
Cysticercosis occurs worldwide but is endemic in countries of Asia such as India; in South America, and eastern Europe, most cases in United States of America are imported. Human Cysticercosis is a major public health problem in Latin America, Africa and Asia and it is a major cause of Epilepsy in Latin American countries where seroprevalence is more than 10% as cysticerci (larval stage of Tapeworms) were detected in 0.1 to 6% of the autopsy cases.
Types of Cysticercosis
- Neurocysticercosis: when it affects the central nervous system
- Ocular cysticercosis: when it affects the eyes and may cause uveitis and retinitis
Cysticercosis Transmission
- Ingestion of larvae in undercooked pork leads to Taeniasis
- Eating food or drinking water contaminated with eggs in the stool leads to Cysticercosis
Cysticercosis Symptoms
- Adult tapeworms infection may not show signs in most cases (they may remain asymptomatic)
- When there are symptoms in Adults worms, they cause loss of appetite (anorexia) and diarrhea
- Some proglottids may be seen in stool
- Cysticercosis in the brain (cerebral cysticercosis) causes headache, vomiting, and seizures
- Cysticercosis in the eyes can manifests as uveitis or retinitis. The larvae can sometimes be seen floating in the vitreous of the eyes of the patients
- Cysticerci may be felt in the Subcutaneous tissue of the skin as nodules
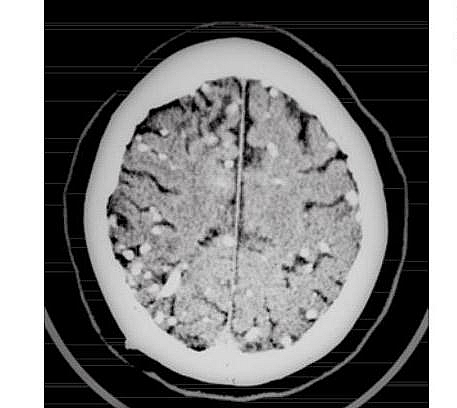
Cysticercosis Radiology and Stages
There are four types of lesions that can be seen using CT scan in cerebral cysticercosis; these lesions occur in phase: vesicular phase, colloidal, granular and nodular phase.
Lesions of the Vesicular phase are minimally enhanced with contrast and appear cyst-like. The colloidal phase shows slight contrast enhancement and there is edema seen surrounding the death cyst. The granular phase shows ring-enhancing lesions while the nodular phase shows a calcified lesion with no enhancement of contrast.
Cysticercosis Diagnostic Tests
- Cerebral cysticercosis can be diagnosed using purified glycoprotein antigens from T. solium metacestodes in a Western blot assay which helps to identify serum antibodies against the parasite
- CT Scan can be used in Neurocysticercosis
- Biopsy of the cyst
- Serologic test such as ELISA that detects antibodies to Taenia solium antigens are available but may be negative in neurocysticercosis.
- Use of Microscope to identify Proglottids in stool
- Eosinophilia is present
Cysticercosis Treatment
- Praziquantel in combination with corticosteroid is the drug of choice and is very effective in treating cysticercosis including neurocysticercosis. This is only effective when calcifications have not formed.
- Albendazole is also used
- Surgical removal of cysticerci even when there is calcification
Cysticercosis Complications
- Epilepsy
- Weight loss
- Uveitis
- Retinitis
- Focal neurological deficits
Cysticercosis Prevention
- Prevention of cysticercosis involves cooking pork properly
- Proper disposal of waste to prevent pigs from ingesting human feces
- Avoid defecating in bushes where animals graze
- Treatment of patients to prevent autoinfection (when a patient becomes reinfected by ingesting food contaminated with their own feces )
- Observe good hygiene by properly washing of hands before eating