Table of Contents
- What is Obstructive Jaundice?
- Obstructive Jaundice Risk Factors
- Obstructive jaundice Pathophysiology
- Causes of Obstructive Jaundice
- Obstructive Jaundice Symptoms and signs (Clinical features)
- Obstructive Jaundice Differential Diagnosis
- Obstructive Jaundice Complications
- Obstructive Jaundice Diagnosis and Laboratory Findings
- Obstructive Jaundice Treatment
What is Obstructive Jaundice?
Obstructive jaundice is a condition of raised bilirubin levels in the blood known as conjugated hyperbilirubinemia that occurs as a result of obstruction to flow of bile due to any cause and preventing bilirubin from reaching the gut (intestines).
Obstructive Jaundice Risk Factors
- High fat diet
- Obesity
- Fair Fertile Female gender
Obstructive jaundice Pathophysiology
Conjugated bilirubin is excreted through the biliary tract to the gut. This helps in fat emulsification and in the absorption of fat soluble vitamins such as Vitamins A, D, E and K.
In the intestine, deconjugation of the bilirubin by intestinal bacteria occurs and it is again reabsorbed into the circulation enterohepatic circulation. Urobilinogen is excreted in urine while Stercobilinogen is excreted in stool and causes the golden brown color of stool.
The obstruction of bile therefore leads to accumulation of conjugated bilirubin in the blood which is then deposited in tissues (causing itching pruritus) and excreted in urine (making dark urine or yellowish urine)
Causes of Obstructive Jaundice
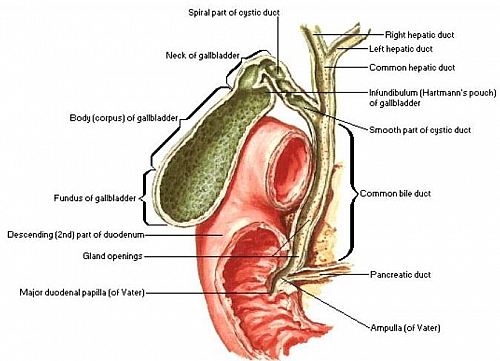
- Gall stones
- Acute Cholecystitis
- Chronic Cholecystitis
- Common Bile Duct obstruction from any cause such as Portal lymphadenopathy ( from cancer of the colon, lymphoma or from Tuberculosis), Carcinoma of pancreas, Carcinoma of the ampulla of vater and Periampullary carcinoma
- Acute gall stone associated pancreatitis
- Sclerosing Cholangitis
- Bile duct strictures
- Mirizzi’s syndrome
- Biliary atresia ( a cause of obstructive jaundice in children)
- Parasites such as ascaris worms and their ova, and hydatid cysts
- Adenocarcinoma of Common Hepatic Duct bifurcation this is also known as Klatskin tumor
- Cancer of Gall bladder obstructing the common bile duct by compression
Obstructive Jaundice Symptoms and signs (Clinical features)
- Jaundice yellowish discoloration of the sclera of the eyes, mucus membranes and skin
- Passage of Dark-colored urine
- Pruritus itching of the skin
- Passage of pale bulky stool (Stearrtorrhoea)
- Fluctuating jaundice with pain and impalpable Gall bladder are suggestive of gall stones
- Dull epigastric pain (upper abdominal pain) that radiates to the back and worsens on lying supine but is relieved on leaning forward and erect this is known as Van zant sign; this sign suggestive of pancreatic cause (acute pancreatitis).
Obstructive Jaundice Differential Diagnosis
- Hemolytic jaundice
- Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C infection
Obstructive Jaundice Complications
- Ascending cholangitis that is characterized by the Charcots triad (right upper quadrant pain, jaundice and fever). This can also lead to hepatic abscesses
- Clotting disorders (Coagulopathy): this occurs as a result of the absence of Bile in the gut leading to non-absorption of vitamin K dependent clotting factors such as Factors II, Vii, IX and XI
- Hypovitaminosis D (Vitamin D deficiency) this can cause disturbance of Calcium metabolism leading to osteoporosis
- Hepatorenal syndrome
- Impaired Drug metabolism with half-life of some drugs being prolonged such as morphine
- Impaired wound healing due to low skin prolyl hydroxylase activity
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Pancreatitis
Obstructive Jaundice Diagnosis and Laboratory Findings
- Urinalysis (Test of urine) for proteins and glucose in urine the presence of urobilinogen means it is hemolytic jaundice while absence of urobilinogen means it is obstructive Jaundice. The presence of bilirubin suggests obstruction as cause of Jaundice.
- Liver Function Test presence of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase indicate obstructive jaundice
- Spiral CT/MRI
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography (ERCP) use for both diagnosis and treatment of obstructive jaundice and other biliary and pancreatic diseases
- Stool analysis the absence of urobilinogen shows there is complete common bile duct obstruction.
Obstructive Jaundice Ultrasound Findings
Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tree will show dilatation of biliary tract of more than 10mm
Obstructive Jaundice Treatment
Treatment for Obstructive is dependent on the cause of the jaundice.
- For Gall stones, treatment is surgery this involves performing cholecystectomy with exploration of Common bile duct or endoscopic papillotomy using ERCP
- For Cancer of head of pancreas, the surgical procedure involves triple or double bypass and in rare early cases of this cancer, a Whipples operation
- For Chronic pancreatitis, a triple or double bypass is done
- For Biliary atresia in children, a Kassai operation is done