Table of Contents
Supraspinatus Action
The Supraspinatus muscle helps to initiate the abduction of the arm before the Deltoid muscle takes over. The supraspinatus also supports the head of the humerus against the glenoid cavity and therefore gives the joint stability during movement caused by actions of other muscles such as the deltoid.
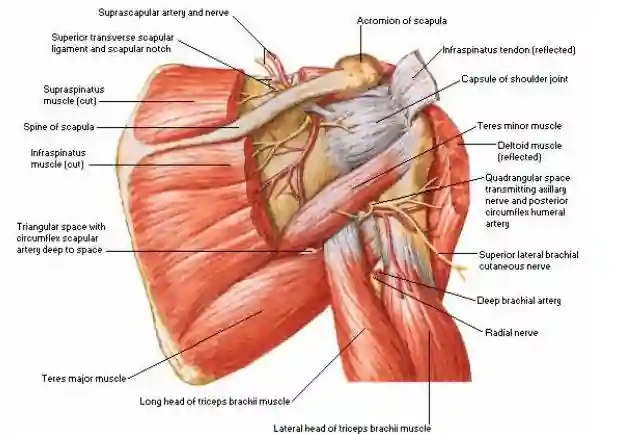
Supraspinatus Origin and Insertion
The Supraspinatus muscle originates from the medial two-thirds of the supraspinous fossa of the scapula (with a bursa separating it from the lateral quarter of the fossa) and inserts at the smooth facet of the upper part of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The supraspinatus tendon blends with the capsule of the shoulder joint.
Supraspinatus Function
The Supraspinatus muscle is part of the rotator cuff muscles and it is the only one among the four rotator cuff muscles that is not a rotator of the humerus but instead initiates abduction of the arm to 15 degrees and assists the deltoid in abduction. As part of the SITS or rotator cuff muscles, it also stabilizes the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity of the scapula during all movements of the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint).
Supraspinatus Innervation
The Supraspinatus muscle is innervated by the Suprascapular nerve (C4, C5, C6) the C5 segment of the spinal cord being the dominant supply to the nerve. The nerve arises from the from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus and passes beneath the superficial transverse scapular ligament to supply the supraspinatus with two branches.
Supraspinatus Blood Supply
The supraspinatus gets it blood supply from the suprascapular artery which is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk while the suprascapular vein drains this muscle by running above the scapula to empty into the external jugular vein.
Supraspinatus Test
The arm is abducted against resistance and the supraspinatus muscle can be palpated (deep to trapezius) above the scapular spine.
Supraspinatus Tendinitis and other pathologies of the supraspinatus muscle
The bursa occupying the lateral third of the supraspinous fossa is clinically known as the subacromial bursa or the subdeltoid bursa, injury to the shoulder or patients who have supraspinous tendinopathy could make this bursa to be inflamed causing pain on movement of the shoulder joint. This inflammation or pain could be treated by use of corticosteroid injection into the area or use of a local anesthetic agent.
Trauma or Injury may cause a tear or rupture of one or more tendons of the SITS muscles with that of the supraspinatus most commonly affected. Also, degenerative tendonitis of the rotator cuff is common in older people.