Tuberculosis Treatment is carried out using the DOTS Therapy which stands for Directly Observed Treatment Short course. The DOTS therapy makes use of antituberculosis drugs over a specified period of time under observation as patients may not comply with drugs which leads to multidrug resistant tuberculosis. The DOTS TB treatment therefore combats resistance.
Table of Contents
- Can Tuberculosis be cured completely?
- Aims of Tuberculosis Treatment
- Tuberculosis Treatment Guidelines
- TB Drugs List and their abbreviations
- Classification of Anti tuberculosis drugs
- DOTS Standard TB Drugs Treatment Combination and Duration
- First Line TB Drugs Dosage and their Side Effects
- Mechanisms of actions of Essential Antituberculosis drugs
- First line Tuberculosis Drugs
- Second Line TB Drugs list
- DOTS Plus TB management
Can Tuberculosis be cured completely?
Tuberculosis can be cured completely when there is compliance with drugs and when it is detected early enough for Treatment to be commenced before any complication develops. Once there is complication, cure for TB can be achieved but some complications may be permanent and can only be alleviated.
Aims of Tuberculosis Treatment
- In order to achieve cure for TB
- To prevent death from active TB
- To prevent complications
- To prevent relapse of TB
- To reduce transmission of TB to other people
- To prevent the development of TB drug resistance, which is a major cause of Multidrug resistant TB
Please note that active tuberculosis treatment should not be initiated with single drug as resistance may occur.
Tuberculosis Treatment Guidelines
- All recommended tuberculosis treatment regimen has 2 phases: the Initiation phase or Intensive phase and Continuation Phase.
- The initial intensive phase is aimed at killing actively growing and semi-dormant tubercle bacilli
- At least 2 bactericidal drugs such as Isoniazid (INH) and Rifampicin are necessary in the initiation phase
- Pyrazinamide given in the initial intensive phase allows the duration of treatment to be reduced from 9 to 6 months.
- Addition of Ethambutol is of benefit when initial drug resistance is suspected or where the burden of organism is high.
Continuation phase aims to eliminate most residual bacilli and reduces numbers if failures and relapse
TB Drugs List and their abbreviations
- Rifampicin (R)
- Isoniazid (H)
- Ethambutol (E)
- Pyrazinamide (Z)
- Streptomycin (S)
- Capreomycin
- Kanamycin
- Viomycin
- Ethionamide
- Rifabutin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ofloxacin
- Rifapentin
- Cycloserine
Classification of Anti tuberculosis drugs
- First line TB drugs
- Second line TB drugs
DOTS Standard TB Drugs Treatment Combination and Duration
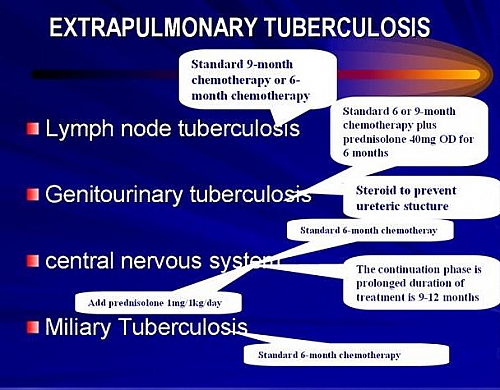
In all cases of Tuberculosis the Standard treatment is applied with addition of few drugs such as: addition of Steroid to Genitourinary TB and Central Nervous system TB. Miliary Tuberculosis, Pulmonary TB and other forms of Extrapulmonary TB all follow the standard treatment outlined below.
Standard 6 months short course chemotherapy
This involves 2 months Intensive phase through the use of:
- Streptomycin or Ethambutol,
- Isoniazid,
- Rifampicin
- and Pyrazinamide
And 4 months Continuation Phase through the use of
- Isoniazid
- Rifampicin
Standard 9 months short course chemotherapy
This involves 2 months Intensive phase through the use of:
- Streptomycin or Ethambutol,
- Isoniazid,
- Rifampicin
- and Pyrazinamide
And 7 months Continuation Phase through the use of
- Isoniazid
- Rifampicin
First Line TB Drugs Dosage and their Side Effects
These are the recommended drugs used in combination as the first in the treatment of active tuberculosis.
Isoniazid Dosage and Side Effects
Isoniazid Dosage
Daily dose of 5 mg/kg oral (maximum 300mg) or (900mg twice weekly or 600mg thrice weekly).
Isoniazid Side effects
- It can cause drug induced Hepatitis
- Can cause peripheral neuritis
- Drug induced lupus
- May cause seizures
- Hypersensitivity with rash and fever
- Involved in drug interactions with dilantin and disulfiram
Rifampicin Dosage and Side effects
Rifampicin Dosage
10 mg/kg oral (maximum 600mg)
Rifampicin side effects
- Orange body secretions
- Flu-like syndrome
- Drug induced hepatitis
- Thrombocytopenia which may cause abnormal bleeding
- Nausea, anorexia and diarrhea
- Renal failure
- Multiple drug interactions
Pyrazinamide Dosage and Side effects
Pyrazinamide dosage
25 to 30mg/kg orally/daily or 30-35 mg/kg weekly
Pyrazinamide Side effects
- Hyperuricemia
- Drug induced Hepatitis
- Body Rash
- Nausea and anorexia
Ethambutol Dosage and adverse effects
Ethambutol dosage
- 25mg/kg daily (orally) for initial 2months of treatment and then 15mg/kg orally for the rest of treatment period
- Or 50 mg/kg twice weekly or 30mg/kg thrice weekly
Ethambutol Side effects
- Optic neuritis
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
Streptomycin Dosage and adverse effects
Streptomycin Dosage
- 15mg/kg given intravenously or intramuscularly (up to a maximum of 1.0g) daily for 5days in a week
- Or 5mg/kg (maximum 1.5g) twice weekly or thrice weekly
Streptomycin side effects
- Ototoxicity
- Vestibular dysfunction
- Nephrotoxicity
- Skin rash
- Hypersensitivity reactions
Mechanisms of actions of Essential Antituberculosis drugs
Anti-tuberculosis drugs have 3 main properties: they have bactericidal activity, Sterilizing activity and the ability to prevent resistance to treatment.
- Isoniazid and Rifampicin are the most potent of the essential antituberculosis drugs that are active against all populations Rifampicin being the most potent.
- Pyrazinamide is most active in acidic environment
- Streptomycin is bactericidal in nature and acts against rapidly multiplying TB bacilli
- Ethambutol and Thiacetazone helps to prevent resistance
First line Tuberculosis Drugs
- Rifampicin
- Isoniazid
- Ethambutol
- Pyrazinamide
- Streptomycin
These 4 drugs for TB that are commonly used as first line TB Drugs. This means when you have tuberculosis, these drugs are used first to treat the TB; if it becomes resistant to treatment, then the second line TB drugs can be used.
Second Line TB Drugs list
- Cycloserine
- Thioamides such as Ethionamide and Prothionamide
- Aminoglycosides: examples include Capreomycin, Viomycin and Kanamycin
- Fluoroquinolones : examples include Ciprofloxacin and Ofloxacin
- Other newer TB drugs include Rifabutin and Rifapentin
DOTS Plus TB management
The DOTS Plus is a strategy for management of cases with multi-drug resistant tuberculosis. It was developed by WHO and partner agencies in 1999 based on the same principle with DOTS.
The DOTS plus includes the use of sputum culture and drug susceptibility test for diagnosis of TB and uses both first line drugs and second line drugs like Ethionamide, Capreomycin, Thiacetacone and Fluoroqiunolones.