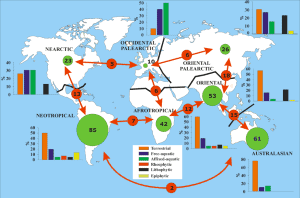
The study of the distribution of animals and plants around the world is known as biogeography.
Biogeography is the investigation of geographical distribution of plants, animals and other living things in an ecosystem.
Biogeography has further two subdivisions:
- Phytogeography is the study of plant distribution on the landscape.
- Zoogeography is the study of animal division on the landscape.
Simply put, it addresses not only residence patterns which has greater impact on the survival of organisms, but also the elements important for distributional variation.
Its objective is to exhibit where species live and why they are in a particular geographic area. Bieogegraophers study the movement of organisms into a range which is called migration.
Table of Contents
- Plant and animal life of a region
- Study of how living things are distributed on earth
- The distribution of related animals and plants across the world
- The geographic study of living organisms
- The study of the distribution of animals and plants around the world
- The study of the patterns in the distribution of plants and animals around the world is
- The study of the spatial aspects of ecology and the distribution of plants and animals is called
- Wildlife factor future
Plant and animal life of a region

Plant and animal life of a region is called biota. Biota is the classification of plants, animals, fungi and all living organisms in an environment that entirely share the same geographical place.
Plant life of a region is known as flora. Flora is plant life occurring in a particular time and area.
Animal life of a region is called fauna. Fauna is all animals in an ecosystem living in a certain time, geological period and region.
Study of how living things are distributed on earth
The study of how living things are distributed on earth is termed biogeography.
The grouping of living organisms existing in various proportions of the biosphere.
The biosphere expands into the airspace to the depths of oceans, basically that’s what makes up an ecosystem.
The definition of an ecosystem is a location on earth that includes all biotic and biotic factors that work in harmony to shape a geological region.
The distribution of biomes is affected by abiotic elements; lands of regions with similar climate, flora and fauna.
The distribution of related animals and plants across the world is proof that all living organisms in a habitat evolved from common predecessors.
Factors that affect the distribution of plant and animal life of a region across the world are:
- the condition of soil
- geological characteristics
- accessibility of supplies
- correlation among preys and predators.
An organisms environment consists of the above factors as well as any various other biotic and abiotic factors.
The geographic study of living organisms
The geographic study of living organisms is biogeography. This includes the study of the distributional make up of species. It also explains how habitats are important for organisms.
This branch has a vital role in grasping the concept of evolution and adaptation of oceans and orgaisms.
The study of the distribution of animals and plants around the world
The study of the distribution of animals and plants around the world is known as biogeography.
Biogeographic study determines the patterns of environmental distribution of all living organisms that inhabit an environment.
For example, biogeography organizes the botanical land of South America as Neotropical. The area where an organism lives in North America is known as Boreal.
The study of the patterns in the distribution of plants and animals around the world is
The study of the patterns in the distribution of plants and animals around the world is biogeography.
Biogeography is about the distribution of all living things in an ecosystem in a geological arena via earthly time.
Life forms with biotic circles usually differ in a systematic manner beside geological gradients of altitude, latitude, solitude including niche regions.
The study of the spatial aspects of ecology and the distribution of plants and animals is called

The study of the spatial aspects of ecology and the distribution of plants and animals is called biogeography.
Biogeography is the study of the apportioning of plants, animals and all organisms that are included in ecosystems.
Scientists that study biogeography or spatial ecology look at the physical and anatomical procedures. They look at how these bring about the distribution of a community in all environments on earth that support life.
Spatial ecology is all about the distribution of organisms affected by both their living and non living environment
Wildlife factor future
Wildlife factor future is a risk factor in the future pandemics.
Research suggests the probability of an infectious agent coming from trading wildlife and farmed animals must be an essential reflection in attempts to stop the upcoming epidemic.