Comparison of monetary vs fiscal policy taking note of the differences and similarities. A simple definition for both fiscal and monetary policies is that they are tools used by government and central banks to regulate the economy in order to control inflation, poverty, unemployment, etc. Below, you will learn the basics of monetary vs fiscal policy simplified in a way that you can understand their importance and impact on the economy.
Table of Contents
- Monetary vs fiscal policy in economics
- Monetary vs fiscal policy chart
- When to use monetary vs fiscal policy
- Monetary policy vs fiscal policy advantages and disadvantages
- Relationship between monetary vs fiscal policy in crowding out and crowding in
- How does fiscal and monetary policy impact the economy?
- How does fiscal and monetary policy influence each other?
- Monetary vs fiscal policy examples
- FAQs on Monetary vs Fiscal Policy
- Resources
Monetary vs fiscal policy in economics
There are two main approaches to the regulation of the economy, these are the use of monetary and fiscal policies. The monetary policy is used by the government to affect the money supply in an economy while fiscal policy deals with government spending and taxation.

What is monetary policy?
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a nation’s central bank (such as the Federal Reserve Bank in the U.S.) with regards to its interest rates, banking system, and availability of cash.
The goal of monetary policy is most often twofold:
- to manage inflation within an economy so as to achieve stable growth, and
- to achieve full employment.
What is fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and tax policies to influence a nation’s economy. This policy has different goals, some of which include: increasing employment, stabilizing prices, reducing poverty, incentivizing investments in research & development, or changing a nation’s distribution of income.
If the economy is overheating (high inflation), fiscal policy can be used to raise taxes or cut spending. This will reduce aggregate demand and slow inflation. The opposite approach can be taken if the economy is heading towards a recession.
Monetary vs fiscal policy chart
Monetary policy is the responsibility of a country’s central bank, while fiscal policy is under the umbrella of the presidency and congress.
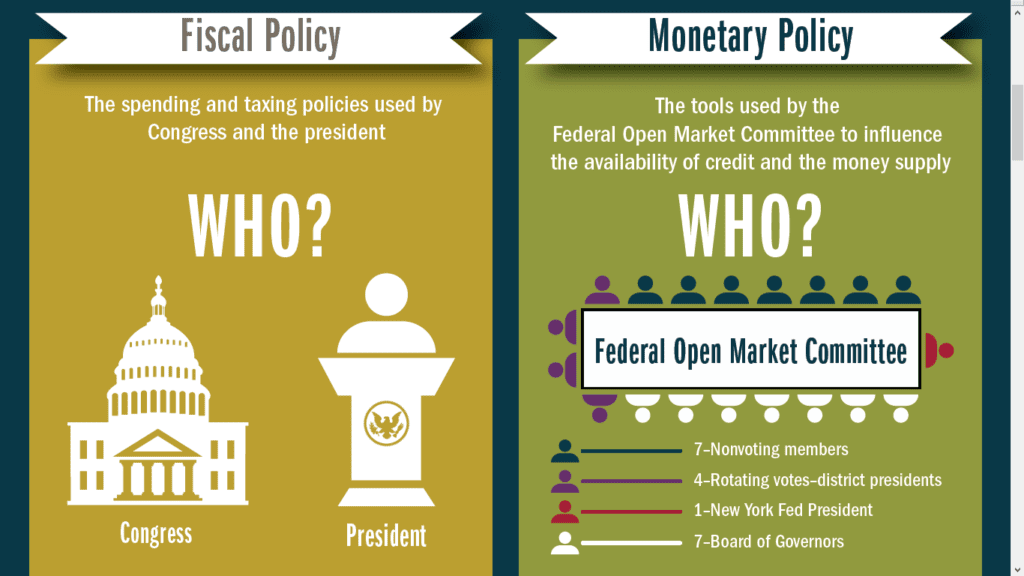
Monetary vs fiscal policy difference chart
When to use monetary vs fiscal policy
A central bank uses monetary policy to meet its objectives, including ensuring price stability and achieving full employment. Instruments include adjusting the interest rates it charges on commercial bank borrowings or undertaking open market operations in which assets are bought or sold.
Fiscal policy is the means by which a government adjusts its spending and taxation in response to changes in economic conditions, and this can be used to stabilize an economy’s business cycle, but this should not be confused with monetary policy, which seeks to control the broad money supply, that is, currency plus bank deposits.
When to use monetary policy
Monetary policy should be used when there is a risk of demand-pull inflation (i.e., inflation caused by a rapid increase in the money supply). For example, when prices are rising because too much money is chasing a few goods and services. Monetary policy can be used to control inflation by raising interest rates, which makes it more expensive for people and businesses to borrow money.
When to use fiscal policy
Fiscal policy should be used when there is a risk of cost-push inflation (i.e., inflation caused by an increase in the cost of production). For example, when workers demand higher wages causing businesses to raise prices to cover their increased costs; in such as situation, fiscal policy can be used to control inflation by increasing taxes, which lowers the demand for goods and services.
Monetary policy vs fiscal policy advantages and disadvantages
The pros and cons of monetary vs fiscal policy and their impact on the economy are all discussed below.
Advantages of fiscal policy
- Fiscal policy advantages stem from its ability to provide countercyclical support for the economy. It can be used to stimulate an economy when the inflation or unemployment rate is too high.
- This method also clears the roadblocks of democracy by getting policies passed through congress since politicians get to decide where and how much funding should go towards certain projects.
- Governments can even use this policy approach aggressively by engaging in deficit spending during bad economic times and in debt servicing if growth returns.
- Fiscal policy deals with both short term and long term growth.
Fiscal policy disadvantages
- One of fiscal policy disadvantages is that it is often a slower approach to economic stabilization in comparison to monetary policy, which can be extremely effective in dealing with inflation and unemployment.
- Another monetary policy disadvantage is that it doesn’t have an effect on long term debt, just the current fiscal year when its implemented .
- In addition, deficits and increased public debt must eventually be paid for by future generations of taxpayers causing interest payments that divert funds away from productive private investments.
Advantages of monetary policy
- An advantage of monetary policy is the provision of flexibility for using discretionary changes in interest rates, open market operations or changing reserve requirements to affect economic activity.
- Monetary policy has an immediate effect on the economy because it can be quickly implemented.
- Additionally, it does not necessarily increase or decrease taxes or government transfers so there are no political ramifications.
- Monetary policy also works independently of financial institutions so they don’t have to agree on changes for things to work.
- Lastly policy decisions do not need to be unanimous, just a majority vote from the Monetary Policy Committee can be accepted.
Disadvantages of monetary policy
- A major drawback of monetary policy is that Central Banks cannot fully control the money supply because it relies upon private sector decisions and liquidity spreads.
- Monetary policy also requires a government to make policy decisions through consensus.
- This policy only deals with the financial sector when using interest rates.
As we can see monetary and fiscal policies each have their distinct benefits and shortcomings; most times, these policies are combined in order to achieve meaningful results.
Relationship between monetary vs fiscal policy in crowding out and crowding in
The crowding out effect occurs when the government tries to increase expenditure on a particular sector but this leads to increased interest rates because there will be limited resources available from the financial market. This leads to an investment-reducing effect, borrowing cost-increasing effect, and consumption-reducing effect since people will have less disposable income due to increased borrowing costs. Crowding out can be used for good and bad depending on the circumstances of the situation.
Crowding-in is when effective use of fiscal policy leads to lower interest rates, which encourages private investment that further boosts demand. When government expenditure increases, interest rates decrease because people will opt for investing their disposable income. The crowding-in effect occurs when the government uses a fiscal policy in an effective way because this will enable people to have more disposable income and therefore increase private investment which further boosts demand, leading to increased economic growth.
How does fiscal and monetary policy impact the economy?
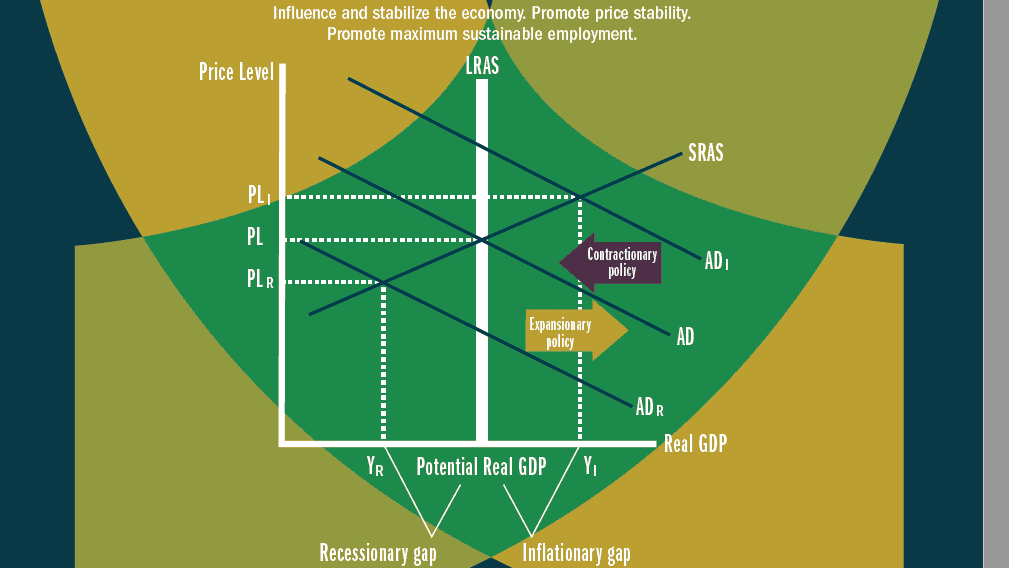
Fiscal policy impacts the economy through its influence on aggregate demand (AD) and potential output (Y*). See how each policy influences these factors as well as their influence on one another below.
How does fiscal policy influence Aggregate Demand (AD)?
Fiscal policy impacts aggregate demand by changing the amount of consumption in the economy. A decrease in taxes results in a higher disposable income, which increases consumption and shifts AD to the right. An increase in government spending increases consumption through its direct effect on demand and also indirectly when it creates jobs for people who have money to spend.
How does monetary policy impact aggregate demand?
Monetary policy influences AD by changing the amount of money that consumers have to purchase goods. An increase in the money supply results in a lower interest rate, which increases consumption by encouraging borrowing and spending. A decrease in the money supply results in a higher interest rate, which decreases consumption by discouraging borrowing and spending.
How does fiscal policy influence potential output (Y*)?
Fiscal policy impacts potential output through its effect on saving. An increase in taxes results in less consumption, which decreases AD and decreases potential output.
How does monetary policy influence potential output?
Monetary policy impacts potential output through its effect on investment. An increase in the money supply increases consumption by making more money available to borrowers, which also raises potential output. A decrease in the money supply decreases consumption by restricting available lending, which lowers potential output.
How does fiscal and monetary policy influence each other?
Fiscal policy impacts the money supply by adding to or draining savings. When the government needs more money than it has available to spend, it turns to the Federal Reserve for a loan. This increases the money supply and lowers interest rates. When the government spends too much money, it must tax more to decrease the money supply and increase interest rates.
How does monetary policy influence fiscal policy?
Monetary policy impacts the budget by changing the amount of money that must be raised through taxes. When the money supply is increased, consumers have more to spend and fewer taxes are collected. This decreases government revenue. When the money supply is decreased, consumer spending decreases, and more taxes revenue is collected.
How does fiscal policy influence monetary policy?
Fiscal policy impacts the money supply when the government spends more than it has available. The government must borrow money to make up the difference, which increases the money supply and lowers interest rates.
Monetary vs fiscal policy examples
Example of how monetary policy can control inflation
The first example of using monetary policy is how it’s used to control inflation. When the economy begins to heat up, the high cost of goods and services rises. One of the most common ways for this to happen is when there is a supply-and-demand issue. There is a high demand for a product, and there is a lower supply of it. When this happens, the price of these goods inevitably increases.
One way that the Federal Reserve can control inflation with monetary policy is to keep the money supply from growing too quickly or too slowly. This will help to decrease both costs and prices as time goes on. The Fed does this by increasing or decreasing the short-term interest rates that are targeted to a specific market. Doing this will decrease the demand for loans, which will indirectly decrease prices and costs as time goes on because people have less money to spend.
Example of how monetary policy can control employment
The second example of using monetary policy is how it is used for controlling employment rates. As we all know, if the economy is growing and people are able to secure jobs at a steady rate, they will be more likely to purchase goods and services which increases the entire economic outlook of the country. If this demand for these goods and services is high enough, then inflation may become an issue as well.
When unemployment levels continue to rise, one of the most common ways that our government can lower it with monetary policy is by decreasing or increasing short-term interest rates as mentioned above. When interest rates increase, borrowing money becomes more expensive and people tend not to want to do it as much. With fewer loans being taken out, there will be less investment in new business which means fewer job opportunities for new graduates. With more and more people giving up on finding jobs, the unemployment rate will go down.
Example of how fiscal policy controls government spending
For fiscal policy examples, we’ll discuss how it’s used to control government spending. Take for instance the Congress approved additional funding for new projects, let’s say Congress allotted $100 million dollars of new spending on some sort of public works project that was going to create 2,000 jobs during this particular time period; then the federal government has two options when it comes down to allocating this money. They could either use tax revenue collected from citizens or issue bonds to do so.
If the government were to choose tax revenue, this would not be an issue because there is currently enough in their account to take care of this new spending level; but if Congress were to pass this spending bill for these new projects and the government does not have enough funds, then the Treasury Department would have to issue more bonds in order for this money to be appropriated. This is where having an understanding of how bond markets work would help us understand why increasing government spending will also increase the national debt because the government would have to pay off these bonds.
When the Treasury Department increases the money supply through the issuing of bonds, then it’s taking up more and more valuable real estate on people’s books as opposed to just using tax revenue. When this happens, there will be a decrease in the value of that bond because more and more people want to own it. If there is a decrease in the value of this bond, then it means that they will not be as valuable if the government needs to sell them back to people.
FAQs on Monetary vs Fiscal Policy
Monetary policy vs fiscal policy, which is quicker to enact?
The monetary policy is quicker to enact since it controls the money supply and is enacted by the central bank through the monetary policy committee. The government controls the fiscal policy which has to be approved by parliament and undergoes protocols that cause a delay in enacting it.
Monetary policy vs fiscal policy, which is better with interest rates?
Monetary policy is better in controlling interest rates and the supply of money and credit, and it is faster to change monetary policies than fiscal policies.
Monetary policy vs fiscal policy, which is better to reduce inflation?
Monetary policy is better than fiscal policy in reducing inflation; it is also less costly and quicker to make an impact than fiscal policy, which does not have a significant effect on the inflation rate.
Fiscal policy vs monetary policy, which is more important?
Most economists believe that both fiscal policy and monetary policy are necessary; and when combined together, the best results are achieved in the regulation of the economy.
What is the relationship between fiscal and monetary policy in developing vs. developed states?
Fiscal and monetary policy are the two main tools used by governments to manipulate their economies. However, they are dependent on the country’s level of development. Developed countries usually have more flexible fiscal policies, while developing countries use more rigid and less effective forms. The reasons for this are complicated and based on the size of the country’s economy (macroeconomic factors), as well as other features such as international trade integration and government effectiveness.
Monetary policy is not as effective a tool in developing countries as it is in developed economies, because developing countries tend to have closed financial markets. In addition, they often have less-developed banking systems and unstable currencies which do not allow for broad quantitative easing during recessionary periods due to inflation concerns.
Resources
- Follow this link to download a PDF file showing a comparison of Monetary vs Fiscal Policy by the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta.