Weather is what we experience in our immediate environment on a daily basis. These experiences are obvious, even without much observation. One can easily detect the changes in the atmosphere whenever they occur, in this case, we can boldly say that the weather has much influence on man and his activity.
Whenever one hears the word “weather“, what should come to the mind should be sun, rain, wind, pressure, humidity, or cloud. It also influences the type of food we eat, the cloth we wear, the places go and where we live.
Table of Contents
Weather definition
This is defined as the condition of the atmosphere at a given time; it is simply seen as the degree at which a place is hot or cold, wet or dry, clear or cloudy, and calm or stormy. Weather conditions make it possible for us to see, feel, and detect each time the changes occur, especially in our immediate environment. Therefore, is simply a day-to-day temperature and precipitation conditions that take place in a given surrounding. This is not the same as climate which takes place over a long period of time.
The climate is defined as the average weather condition of a place over a given period, usually over 30 years. Weather changes on a daily basis it could be minute by minute, hourly, daily, weekly, monthly or yearly, while climate changes after a long period of time, hence, climate change is the rise in average weather condition over time and space.
Elements of weather
Common elements of weather include Precipitation, temperature, humidity, cloudiness, atmospheric pressure, and wind. They are what bring about sudden atmospheric changes.
- Precipitation – precipitation is a form of water in the atmosphere that falls to the earth; it is formed as a result of rapid condensation of moisture. This falls after the cloud has been formed in the sky. The forms of precipitation include rain, snow, fog, mist, hail, sleet, and drizzle. As an element of weather, precipitation determines whether outdoor activities are suitable and it can easily be predicted by observing the signs in the sky.
- Temperature – temperature measures the degree of hotness or coldness of a place from day-to-day. Increased temperature is determined by the angle of the sun hence, the temperature may change repeatedly within a day. However, the temperature is an important element of weather and influences other elements such as wind, humidity, precipitation, atmospheric pressure, and clouds.
- Humidity – is simply the amount of water vapor in the air or in the lower atmosphere. The humidity is an element of weather that can influence the day by making it feel hotter humidity. It can be used to predict a coming storm. However, humidity is the prolonged moisture level of an area that can affect an entire ecosystem.
- Cloudiness – this is simply the state of clouds in the atmosphere in a given time over an area. Different types of clouds mean different weather conditions. For instance, lighter cloud indicates little or no precipitation, while dark heavy cloud indicates that the will be heavy rain or thunderstorms.
- Atmospheric pressure – the atmospheric pressure is the “weight” of the air in the atmosphere. Changes in atmospheric pressure are mostly caused by the rise of warm air and the descent of cold air; hence, atmospheric pressure occurs mostly in regions near water bodies. For instance, coastal regions and islands on a daily basis experience severe storms as a result of nearness to water bodies.
- Wind – is the air in motion that moves from areas of high air pressure to those of low air pressure, wind occurs due to rising hot air or sinking cold air.
Elements of Weather and the Instruments used in their measurements
These are the common weather elements and the common instruments used in measuring them.
Precipitation
Precipitation is measured with a rain gauge. The rain gauge measures the amounts of water that falls at a particular time. There are two major types of rain gauges used in weather observations: a tipping bucket and a weighing rain gauge.
Temperature
A thermometer is used to measure the temperature of the day (especially the maximum and minimum temperatures). Most thermometers are closed glass tubes that contain liquids such as alcohol or mercury. It uses units such oC or oF and K. The thermometer is usually kept six feet above ground in a white box to record the temperature of the day thus, keeping the sensor in the shade.
Atmospheric pressure
This is measured with the used of an instrument called a Barometer. The barometric pressure is influenced by the local weather. Rising pressure is an indication of fair weather while falling pressure is an indication of poor weather.
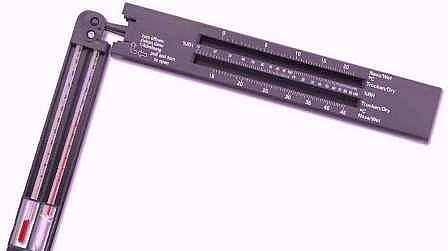
Relative Humidity
The humidity is measured with the use of a hygrometer. This instrument measures the water vapor content of the air, while a sling psychrometer measures relative humidity, using the cooling effect of evaporation.
Wind
Measuring the wind as an element of weather includes measuring the speed and the direction using two different instruments. An anemometer is used to measure wind speed while a wind vane is used to measure wind direction.
Cloudiness
The cloud is measured with a device called a Ceilometer. The ceilometer is used to determine the height of the cloud and also used for determining of aerosols concentration in the atmosphere.
Other weather instruments and their uses
Weather balloon
A weather balloon is used to measure the various conditions higher up in the atmosphere. It can go as high as 20-30 km. A weather balloon is made of rubber and has a weight of only about 200 grams. The skin of the weather balloon is very sensitive and delicate, so they must be touched only when wearing protective gloves to prevent damages.
Weather satellite
This is an instrument used for photographing and tracking of large-scale air movements. After the air has been tracked and photographed, a meteorologist compiles and analyzes the data with the help of a computer.
Disdrometer
A Disdrometer is a device for analyzing the volume of distribution of microparticles in a controlled environment. The main application is to determine the size, speed, and the number of raindrops. With the use of a disdrometer the meteorologist is able to differentiate raindrops from hail.
Lightning detector
This device is used for detecting lightning or light rays that are produced by storms.
Snow gauge
A snow gauge is an instrument used for measuring the water equivalent of an amount of snowfall.
Weather radar
This is a type of radar used in meteorological stations to locate precipitation, calculate its trajectory and estimate their types (rain, snow, hail or fog), it is also used to detect of hazardous weather, such as a thunderstorm, powerful clouds, hail, and heavy precipitation zones.

 Picture of rain gauge – an instrument of weather for rainfall (precipitation) measurement
Picture of rain gauge – an instrument of weather for rainfall (precipitation) measurement