The central vacuole function and structure in plant cells are distinct from other cell types. Plant cells differ from other living cells because they contain chloroplast and can manufacture their own food. This kind of cell has a large central vacuole and a cell wall that plays a role in the structural integrity of plants.
Plants need to store water and other materials for growth and several functions. As a result, they make use of the large central vacuole located at the center of their cell for some of their cell activities. It is said that the large central vacuole of a plant cell occupies about 80% or more of the cell.
This article covers the structure and function of central vacuole in a plant cell. First of all, let’s look at the definition of a central vacuole.
Table of Contents
What is a central vacuole?
A central vacuole is a large vacuole in the cells of plants that are filled with fluids and molecules. The large central vacuole definition in biology can be described as a membrane-bound sac within the cytoplasm of the plant cell that is made up of cell sap and tonoplast. The central vacuole in a plant cell is surrounded by the cytoplasm of the cell.
In organisms, various types of vacuoles can be found which include the central vacuole, food vacuoles, contractile vacuoles, and gas vacuoles. The large central vacuoles are only found in plant cells whereas other vacuoles can be seen in protist, animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Generally, the function of vacuoles in cells includes water storage, turgor pressure in plants, and endocytosis and exocytosis in animal cells. The central vacuole in a plant cell is large and can be single compared to other living cells. For instance, the vacuoles in animal cells are smaller and multiple which are used to temporarily store materials or to transport substances.
The large central vacuole, cell wall, and chloroplast are distinct structures found in plant cells. Basically, the storage of water, as well as enzymes, pigments, and waste is the large central vacuole function in a plant cell. The plant cell’s central vacuole is surrounded by a phospholipid membrane and serves as a storage tank for water and other molecules. Central vacuole storage of water is what causes the turgor pressure exerted on the cell wall which gives the plant cell rigidity.

Therefore, the main role of the central vacuole in plant cells is to store water and maintain the turgor pressure in the cells. Moreso, the central vacuole in plant cells helps to push the cellular contents towards the cell membrane in order to allow the plant cell to absorb more energy from the sun to manufacture food through photosynthesis.
Central vacuole structure
The large central vacuole of a plant cell occupies the center of the cell and is surrounded by cytoplasm. Therefore, in the structure of plant cells, the large central vacuole location is the center of the cell. The central vacuole structure is prominent in the cell. In a plant cell, the structure of the central vacuole is made up of two parts which include the tonoplast and cell sap. Therefore, the central vacuole is enclosed by the tonoplast which is an essential component of the plant endomembrane system.
The tonoplast is also known as the vacuolar membrane and is the membrane of the central vacuole. Whereas, the cell sap is the fluid within the vacuole which consists mostly of water and other constituents like salts, ions, nutrients, waste products, and sometimes pigment molecules. Technically, the tonoplast serves as the vacuole membrane, and similar to the cell membrane, it is made up of phospholipids and proteins. The proteins in the tonoplast can control the entry and exit of water in the vacuole. Moreso, these proteins regulate the movement of ions such as potassium. Basically, the tonoplast of the vacuole separates the contents of the central vacuole from the rest of the cell.
As the plant cell matures, the large central vacuole structure slowly develops by the fusion of smaller vacuoles derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. The central vacuole in plant cells is highly selective in transporting material through its membrane. This is why the chemical palette of the cell sap of the plant cell’s central vacuole differs markedly from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The large central vacuole of plants can even contain pigments that give certain flowers their distinct colors. In some plants, the large central vacuole structure constitutes plant wastes that are bitter and unpalatable to insects and animals. Furthermore, the central vacuole in a plant cell of a developing seed can be used as a structure for protein storage.
The central vacuole diagram
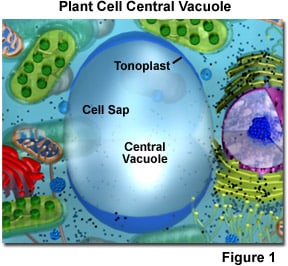
The structure of the central vacuole consist of a tonoplast and cell sap
Photo credit: www.micro.magnet.fsu.edu
Microscopy
The structure of the central vacuole under a microscope may appear like a space in the plant cell bounded by a single membrane. Firm small onions are preferable for microscopy of the central vacuole of plant cells. In order to view the onion epidermal cell central vacuole, remove the epidermal layers by cutting the onion and peeling them off. The epidermal layers are membrane-like sheaths between each onion layer. Viewing the layers halfway between the outside and center of the onion is usually best for advanced microscopy such as fluorescence microscopy.
Central vacuole function
- One major function of central vacuole is to maintain the turgor pressure in plant cells which gives the plant rigidity.
- The central vacuole in a plant cell plays an essential role in facilitating photosynthesis.
- Storing ions and enzymes needed for the cell’s metabolism is a major role of central vacuole in a plant cell.
- Another role of the central vacuole in plant cells is to serve as storage vessels especially for water storage.
- The plant cell’s central vacuole regulates the osmotic potential.
- The storage of colored pigments such as in the petals of plants.
- Molecular degradation is another central vacuole function in a plant cell. The central vacuole can serve as a compartment where materials are broken down similar to the lysosomes in animal cells.
- Storage and disposal of metabolic waste are also the functions of central vacuoles in plant cells.
Vacuoles as membrane-bound sacs within the cytoplasm of the plant cell function in several different ways. The plant cell’s central vacuole is very large and serves a wide range of functions, both structural and physiological. It is extremely important in providing structural support, as well as serving functions such as storage, waste disposal, protection, and growth. Discussed below are the main functions of the large central vacuole of plants:
Facilitates photosynthesis in plants
The central vacuole in a plant cell plays an essential role in facilitating photosynthesis. In plant cells, the central vacuole functions in storing essential molecules. Central vacuoles can take up 80% or more of the plant cell’s space, pushing other organelles of the cell closer to the cell membrane. Therefore, pushing the chloroplasts to the edges of the cell for maximum absorption of sunlight.
The chloroplasts in the plant cell are then able to get maximum exposure to sunlight which is essential because photosynthesis takes place in these organelles. Photosynthesis is the process whereby nutrients are produced in the presence of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Sunlight is absorbed by chloroplast in order to obtain energy for photosynthesis.
As the vacuole pushes chloroplasts closer to the surface of the cell, more solar energy is absorbed, thus facilitating photosynthesis in plants. Moreso, the necessary molecules that play a primary role in photosynthesis such as nutrients, water, ions, and enzymes can be transitionally stored in the vacuole. These substances are stored in the vacuole until they are needed and then sent back into the cytoplasm.
Storage of water, ions, pigments and essential molecules
The main role of the central vacuole in plant cells is to serve as storage vessels for mostly water, as well as salts, minerals, nutrients, proteins, pigments, etc that aids plant growth. These stored materials play an important structural role for the plant. The central vacuole storage of ions, proteins, sugar, and enzymes is also essential for the cell’s metabolism.
Occasionally, pigments are stored inside the vacuole. For instance, flower petal cells get their characteristic color from the pigments produced and stored in the central vacuole. The pigments stored in the vacuoles give certain flowers colors, aiding the plant in attracting bees and other pollinators. Moreso, some poisonous materials, that would harm the cytoplasm, are excreted into the vacuole. The storage of these poisons in the vacuole makes the plant unattractive and unpalatable to herbivorous animals.
Also, waste products and nutrients are stored temporarily in the vacuole and the concentration of these substances affects the turgor pressure in plants. When there are molecules other than water in the central vacuole, turgidity decreases. As a result, the central vacuole in plant cells must always have a much higher concentration of water than any other molecule. However, the majority of the materials commonly stored in the plant vacuoles have been discovered to be useful for humans e.g rubber, opium, and garlic flavoring. Such materials are frequently harvested by humans.
The central vacuole storage of water helps maintain the high turgidity that plants need. As the central vacuole in the plant cell stores water, it swells up so that the cell can maintain the high turgidity required for optimal functionality. The central vacuole storage of water plays a role too in the shape of the cell because as the vacuole is filled tight with water, it exerts a turgor pressure that holds the cell firm. It is this effect that gives the characteristic shapes of plant structures such as leaves. This is why a leaf wilts when the plant has been without water for a long time. The wilting of the leaf occurs because the cells lose shape as the vacuole loses water.
Disposal of metabolic waste
Through the phospholipid bilayer membrane (tonoplast) of the central vacuole, molecules are selectively exchanged between the vacuole and cytoplasm. This helps to create an optimal chemical environment within the cell.
In plants, the large central vacuole function in the storage and disposal of metabolic waste. Through metabolic processes, plant cells produce many by-products. Some of these by-products are undesirable waste products. As a result, there are adverse effects that occur from the presence of these undesirable waste compounds in the cytoplasm because these compounds can interfere with essential reactions in the cell.
Furthermore, damaged cell organelles can hinder the cell from functioning properly. Therefore, in order to prevent this, the central vacuole safely stores damaged cell organelles and waste compounds. The waste trapped in the vacuole can eventually be disposed of when a leaf withers and falls off the plant. Disposal of waste products is thereby an essential central vacuole function in a plant cell.
Maintenance of turgor pressure in plants
The function of the central vacuole in plants involves the maintenance of the turgor pressure. Maintaining the turgor pressure in plants gives the plant rigidity. When water fills the central vacuole, pressure is exerted against the cytoplasm and other organelles of the cell. This pressure is what is known as turgor pressure.
The pressure pushes cell organelles against the cell wall and provides rigidity to plant cells which allows the plant structure to support itself. Moreso, this turgor pressure caused by the central vacuole allows cells to grow during cell expansion when the cell wall is temporarily weakened by enzymes. A water-filled vacuole exerts turgor pressure on the cell wall of plants which makes the cell turgid.
Turgor pressure is only found in cells with cell walls such as fungi, bacteria, and plants. Changes in the turgor pressure of a cell occur due to osmosis which is the diffusion of water into and out of the cell. A plant cell in a hypotonic solution has a higher concentration of water molecules outside the cell than inside the cell and as a result, water flows into the cell. This causes water to fill the vacuoles of plant cells making the cell have high turgidity which is the optimal condition for plant cells.
In an isotonic solution, the concentration of water molecules within and outside the cell is roughly the same. Therefore, the amount of water that exits and enters the cell is the same. In such a solution, plant cells become flaccid and start to droop. For a hypertonic solution, there is usually more water inside a cell than outside the cell. Hence, water flows out of the cell causing the plant to wilt and possibly die.
Plant cells thrive in hypotonic solutions rather than in isotonic or hypertonic solutions because even with excessive water intake, their cell walls prevent them from bursting. Animal cells, on the other hand, do not have cell walls and are fare best in isotonic solutions. This is because if these cells are in hypotonic solutions, too much water will enter the animal cell and cause it to burst. Nevertheless, in a hypotonic solution, the function of the central vacuole in maintaining the turgor pressure is very essential.
However, the vacuole can shrink when a plant is deprived of water which makes the vacuole unable to exert turgor pressure. Hence, the plant cell loses its rigidity and becomes flaccid. It is as a result of this loss of rigidity that plants wilt when they are deprived of water for long. This simply means that loss of water from the central vacuole causes no turgor pressure which results in a flaccid cell.
The plant, Mimosa pudica (touch-me-not plant) is a typical example of how plants tend to use the vacuole to voluntarily regulate the turgor pressure of cells in order to carry out a specific function. Once, you touch the leaf of a touch-me-not plant, it sends a signal to the cells at the base of leaflets.
This signal stimulates the exit of water from the vacuoles of these cells. This eventually causes a rapid loss of turgor pressure in these cells. Thus, the cells become flaccid and they are unable to hold the leaf open, causing the leaf to fold. This feature makes the plant appear less appetizing to herbivores and they tend to escape being eaten.
FAQs
What does central vacuole mean?
A central vacuole is a large vacuole in the cells of plants that are filled with fluids and molecules. It can be described as a membrane-bound sac within the cytoplasm of the plant cell that consists of the cell sap and tonoplast.
What is the central vacuole function?
The primary function of the central vacuole in a plant involves the storage of water, ions, enzymes, pigments, and waste products. Other functions include maintaining the turgor pressure in plant cells, facilitating photosynthesis, molecular degradation, and disposal of metabolic waste.
Do animal cells have a large central vacuole?
Animal cells have vacuoles but do not have large central vacuoles like plant cells. The central vacuole in a plant cell is large and single whereas animal cells have multiple small vacuoles in a cell.
What would happen to the size of the central vacuole of a plant that doesn’t have enough water?
The size of the central vacuole shrinks when a plant is deprived of water. As a result, the vacuole is unable to exert turgor pressure making the plant cell lose its rigidity and becomes flaccid. It is as a result of this loss of rigidity that plants wilt when they are deprived of water for long.
Who discovered the central vacuole?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, inventor of the microscope, discovered vacuoles in 1676. The Dutch scientist discovered not just vacuoles but many other cellular structures.
What happens to turgor pressure when the central vacuole fills with water?
When the central vacuole is filled with water, the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall by the vacuole becomes high. As water fills the vacuole, the turgor pressure within the cell is increased. This turgor pressure together with the cell wall’s support helps in maintaining the structural integrity of the plant.
Which type of cell has a large, central vacuole that controls water pressure?
Plant cells have a large central vacuole and a cell wall that plays a role in the structural integrity of plants. They are distinct from other cell types most especially because they contain chloroplast and can manufacture their own food.
In addition to water, what would most likely be found in a plant central vacuole?
Other materials such as salts, minerals, nutrients, proteins, pigments, and metabolic waste in addition to water can be found in a plant vacuole.
If a cell had a damaged central vacuole, it would have difficulty performing what function?
If a cell has a damaged central vacuole, it would have difficulties storing water.
What are the two roles of the central vacuole in plant cells?
The main role of the central vacuole in plant cells is to serve as storage vessels and maintain the turgor pressure in the cell.
What does a plant’s large central vacuole hold?
The plant’s large central vacuole holds water, molecules, and dissolved substances.
Do both plant and animal cells have a central vacuole?
No. Plants have a central vacuole whereas the vacuoles of animal cells are not as central and large as plants own. An animal cell has many smaller vacuoles.
What is the function of the central vacuole in plant cells?
The role of the central vacuole in a plant cell is to store water and other necessary materials.
What is stored in the central vacuole?
The central vacuole can store water, salts, minerals, nutrients, proteins, pigments, damaged organelles, and metabolic waste in the cell.
In a plant cell, where is the central vacuole located?
The central vacuole is located at the center of the plant cell.
What does the central vacuole do?
What the central vacuole does in the plant cell is store water, ions, enzymes, pigments, damaged organelles, and waste products. Other functions include turgor pressure maintenance in plant cells, facilitating photosynthesis, molecular degradation, and disposal of metabolic waste.
Can you see a central vacuole with a compound microscope?
Yes. In the majority of plant cells, the organelles that are visible under a compound light microscope include the central vacuole, cytoplasm, cell wall, cell membrane, and nucleus.
Do all plant cells have a large central vacuole?
The majority of plant cells have a large single central vacuole that takes up 80% or more of the space in the cell.
How does the cell wall and central vacuole contribute to the support of the plant?
As the plant takes in an adequate amount of water, the vacuole of the plant cell swells. Due to the water collected within the vacuole, a high level of turgor pressure is created. During this, the vacuole exerts a significant turgor pressure against the cell wall of the plant. This pressure determines the cell rigidity and is associated with the difference between the intracellular and extracellular osmotic pressure of the cell.
Therefore, the turgor pressure exerted by the vacuole helps to maintain the structural integrity of the plant together with the cell wall’s support. This means the turgor pressure is an efficient way for plants to structure themselves even though they can droop when the pH balance is off or they lack enough water. In order words, the structural relevance of the vacuole in plant cells is associated with its ability to control turgor pressure.
What cells would have a nucleus, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole?
Plant cells.
Where is the central vacuole located in a plant cell?
The central vacuole is found in the center of the plant cell surrounded by the cytoplasm.
What happens if the central vacuole is defective?
The vacuoles in plants play a major role in water storage and structural maintenance. Therefore, if a cell has a defective vacuole, it would not be able to carry out its usual functions and would eventually die.
What does a central vacuole look like?
A central vacuole looks like a membrane-bound sac filled with water.