Table of Contents
What is an ocean?
An ocean is the wide open mantle of water surrounding the continents. The oceans and seas cover 71% of the total earth surface which means that the dry land area only occupies the remaining 29% of the surface of the earth.
Even though the decline of sea travel and diminishing dependence on self-supplied food sources has removed the maritime world from the realm of landlubbers everyday experience, the sea remains a crucial domain for the essential wherewithal that sustains humanity. Three perspectives have dominated most studies of humanmarine interactions: the ocean as a resource provider, the ocean as transport surface, and the ocean as a surface for moving troops and projecting military power. Embedded in each of these analytical perspectives is a certain conception of ocean space and ocean governance. The value of the oceans to mankind has political, social, economic, ecological and cultural dimensions. Marine industries include fisheries, mining, non-conventional energy industries, fresh water production, coastal services, environmental services, trade, tourism, sub-marine telecommunications and fibre optic cable, safety and salvage, naval defence and ocean-related education, training and research. The economic importance of the oceans is immense.
However, there are 5 major oceans in the world, the Pacific ocean is the largest ocean in the world, it occupies an area 165 million km2 with an average depth of 3,970m.
The ocean basins of the world are large depressions on the earths surface which are filled by a great mass of salt water. The ocean water and the movement of the water are under the course of study known as oceanography; the ocean is often studied by oceanographers. The ocean has a significant effect on thebiosphere. Oceanicevaporation, as a phase of thewater cycle, is the source of most rainfall, and ocean temperatures determineclimate andwindpatterns that affect life on land. Life within the oceanevolved3 billion years prior to life on land. Both the depth and the distance from shore strongly influence thedistributionof the plants and animals present in each region
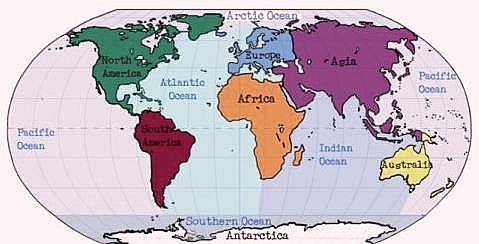
Five Oceans of the world
There are five (5) major oceans of the world and they are as follows:
- The Pacific Ocean
- The Atlantic Ocean
- The Indian Ocean
- The South Ocean
- The Arctic Ocean
The Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of all the ocean basins in the world. The pacific ocean basin occupies 1/3 of the total earth surface. In size, it measures about 85 million km2. However, the Pacific ocean is far bigger in size than every other continent in the world. In depth, it has a maximum depth of 4,280 meters.
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic ocean is the second largest ocean in the world, it is located between Africa and Europe , the east and America to the west. It is the busiest sea routes ocean in the world with a total area of about 65 million km2 and an average depth of about 3,646m. It narrows in equatorial latitudes and this has made it possible for the two basins, the north Atlantic and the South Atlantic basins. In the northern hemisphere, a larger part of the continental shelf occurs, for instance in the North-Western Europe and around Newfoundland as well as the maritime parts of Canada. There is a broad shelf off Patagonia in the southern hemisphere. However, apart from the places mentioned above, continental shelf is narrow elsewhere for example the blocks of Africa and Brazil.
Indian Ocean
Indian ocean occupies an area of about 74 million km2 . Comparatively, it is smaller in size than the Atlantic and totally different from the other three main oceans because it is wholly enclose to the north and lies mainly in southern hemisphere. The Indian ocean is bounded in the west by Africa, in the east by Australia and by Asia in the north and to the south by Antarctica. It has an average depth which total about 3,741 metres.
The South Ocean
The Southern Ocean is recently included among the oceans of the world. The Southern Ocean is recently recognized by theU.S. Board on Geographic Namesas the body of water that stretches from the coast of Antarctica in its entirety. It has an area of 21 million km2. It was not quite long just around the year 2000 that the South ocean was included as the fifth ocean, hence it was officially given the name South Ocean The South Ocean extends out to 60 degrees South latitude. Its has an extreme environment and it is the least understood of the 5 oceans; this is because it is unexplored, far from populated areas and has a severe climate.
The Arctic Ocean
The arctic ocean occupies the area around the north pole. It is a shallow basin with an average depth of 1,205metres and it occupies an area of 15 million km2. The southern part of this ocean is surrounded nearly all over by North America and Eurasia.
The Ocean Floor
The relief of the ocean floor is as varied as that of the land surface. The five major ocean floor relief are:
- The continental shelf
- The continental slope
- The deep sea plain
- The ocean ridge
- The ocean deeps
The continental shelves
These are the areas of shallow water which surround the continent. The continental shelves are wider in some areas of the world such as the edges of the Arctic oceans, areas between the sea of Japan and the Islands of Java and Sumatra, areas between Australia and the Island of New Guinea. Elsewhere around the continent, continental shelves are fairly narrow. One of the major importance of continental shelves to man is that they provide good fishing ground for man. The shallow nature of the water allows sunlight to penetrate through it and the formation of plankton, an essential fish food also takes place. Secondly, the shallowness of the continental shelves make it easy for the exploration of crude oil ( petroleum in the area. Again, continental shelves bring about the development of natural harbour as this is seen in the seaports of Southampton, Hamburg and Singapore. Lastly, continental shelves bring about development of tourist centres.
The deep sea plains
These are wide, gently undulating or fairly level surfaces which have a depth of between 2000m and 3000m, these are also referred to as Abyssal Plain.
The ocean ridges
The ocean ridges take the form of either a ridge or a plateau. These ridges rise up from the deep sea pain. Some of them rise above the surface to form oceanic islands. Some of ocean ridges are the mid-Atlantic ridges and Albatross Plateau.
The Ocean Deeps
These are very deep trenches in the floor of the ocean, they are located close to the continent with about 9000m or more in depth and may run for thousands of kilometres. They can be found in areas very close to young fold mountain chains. Examples of these are the Mariana Trench, Atacama Trench which are all found in the Pacific Ocean just to the west of the Andes Mountain.
Importance of Ocean
- Oceans provides food for man in form of proteins (fish, crabs, shrimps, crayfish, periwinkles) Etc.
- Oceans creates opportunity for educational research based on the aquatic plants and animals found there, this is often carried out by oceanographers.
- Oceans serve as the major source of salt extraction and other mineral resources.
- Oceans are often used worldwide as a means of transportation and communication between countries and continents.
- Oceans of the world make international trade to be possible between different countries of the world.
- Oceans often provide employment opportunities for sailors, fishermen and boat builders.
- Oceans often provide beautiful scenery which attracts tourists all over the world.
- Oceans bring about the development of seaports. However, seaports simply refers to the terminal point for ships. Example is the Tin Can Island Port in Lagos, Nigeria.