Table of Contents
What is IVF?
IVF means In-Vitro Fertilization. Vitro means glass, hence In-vitro Fertilization is the process of fertilizing an egg using sperm in a glass tube. Ever since the birth of the first baby in England in 1978 by IVF, and also in the United states of America in 1983, several fertility centers all over the world have had high success rates and have added laughter to many families across the world.
IVF is a form of assisted conception or assisted reproductive technology where by eggs (ova) are collected from the womans body through surgery and are then placed in a specialized glass together with sperm collected from the man. The sperm then fertilizes the eggs and they start the process of becoming a baby. The early division of the fertilized ovum (called an Embryo) is then placed inside the womans womb (uterus) in order for the baby to develop normally. IVF comes with associated risks, complications and has different success rates. Not all women who are infertile can have IVF done but there are indications or requirements and IVF is costly which may not be affordable to even those that are eligible for the procedure.
Steps involved in carrying out IVF
- Superovulation (Ovulation induction)
- Collection of eggs
- Insemination
- Embryo transfer
- Luteal support
- Pregnancy test
Induction of ovulation in IVF
This process involves the stimulation of your ovaries to produce eggs. The drugs used for stimulation of the ovaries are known as Gonadotropins; clomiphene citrate can also be used or a combination of clomiphene citrate and gonadotropins. When the ovaries are stimulated, it can become over stimulated and may lead to a condition known as hyperstimulation syndrome. It is a common complication of IVF. In order to avoid the hyperstimulation syndrome, careful monitoring of the eggs in your body while they are being produced is done using ultrasonography and the amount of estradiol in the blood is also used to monitor the effect of superovulation during IVF. When the stimulated eggs are greater than 18mm in size and about 34 to 38 hours prior to the time that the eggs will be harvested, a hormone known as Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hcG) is given.
Procedure for collection of eggs from the woman during IVF
Eggs are collected by two ways depending on how advanced the fertility center or hospital is. Some IVF centers use surgery to remove the eggs while others use an advanced procedure known as ultrasound guided transvaginal follicle aspiration. When collected, the eggs are placed in a culture medium that contains the necessary nutrients needed for fertilization to occur and for the embryo to grow properly. The culture medium is then maintained at a temperature of 370 C and pH is maintained using 5% carbon dioxide.
Equipment and procedure for insemination in IVF
- Petri dishes
- Multi well dishes
- Test tubes
- Central well organ culture dishes
Insemination
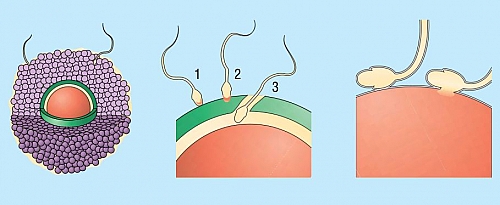
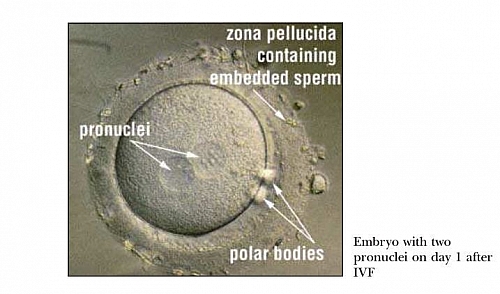
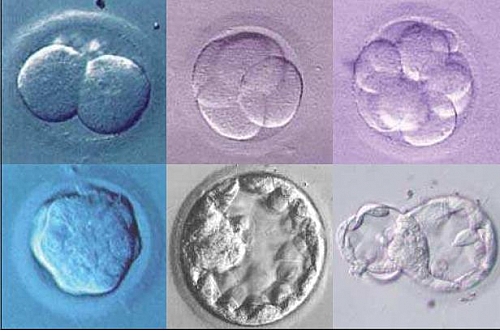
Each egg collected is then placed in a different dish and to each egg, about 50,000 to 100,000 normal sperm cells are added to enable fertilization. About 12 to 20 hours after adding the sperm cells to each egg, fertilization can be observed by the presence of two pronuclei in each egg and also the presence of two polar bodies located in the perivitelline space. The fertilization rate can be as high as 60%; which means that, if 100 eggs were collected, then 60 can become fertilized. If the sperm cells or eggs are not normal, then fertilization may not occur. The cells start to divide every 24 hours after insemination. The cells divide to a two cell stage, 24 hours after insemination, and then to a four cell stage after another 24 hours and so on. Because the fertilization and culture of the embryo in the laboratory is done in tubes, the babies produce by IVF are often informally referred to as Test Tube Babies but are normal babies and can be as intelligent as any other baby. They are not in any way less or inferior.
Embryo transfer
About 2 (four cell stage of division) to 3 (six or eight cell stage) days following insemination, the embryos (fertilized ova) are then transferred into the womb of the woman. The more the cells are allowed to divide, the better the chance of selecting competent embryos for transfer; though it is preferable the transfer should not be allowed to past the blastocyst stage (day 5 after insemination).
About 2 or 3 embryos are transferred into the womb (uterus) of the woman using soft plastic embryo transfer catheter and ultrasound may be used to guide the correct transfer of the embryo. This procedure may not be painful and you can go home a few minutes after the procedure. If there are excess of the good embryos following insemination and transfer, they can be stored by cryopreservation for subsequent IVF procedure. Cryopreservation is a form of storage where the eggs are frozen for future use.
Luteal support in IVF
Following ovulation in normal menstrual cycle, the ovaries produce progesterone, a hormone that helps in maintaining pregnancy; this does not occur in all cases of IVF, hence, the pregnancy needs to be supported by giving progesterone to increase the success rate and prevent failure. Most IVF centers or clinics give this in the form of progesterone tablets, pessaries, suppositories or injections.
Pregnancy test
A pregnancy test is done about 14 days after the embryo transfer
Who is eligible for IVF?
Not everyone with infertility should have IVF done; there are indications for the procedure which are listed below.
Indications for IVF
- Damage of a womans fallopian tubes due to any cause such as severe infections
- Woman having no fallopian tubes due to removal during surgery following cancer or complicated ectopic pregnancy
- Women having infertility as a result of endometriosis
- Infertility of unknown cause
- Infertility following hostility of the womans immune system against the sperm
- Mild male infertility
- Unsuccessful Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
If a woman with infertility has any of the above or a man with infertility who has low sperm count or higher abnormal sperm compared to the normal sperm, then the couple can have IVF done if they can afford the cost of the procedure.
IVF success rates
The success rate or pregnancy outcome of IVF is determined based on various factors. The success rate can be determined using the number of IVF cycles before the woman gets pregnant. If a woman gets pregnant after 1 cycle of IVF; it means then that the success rate is 100% for that specific woman; this may not be the case in all situation and some women may have to undergo more than one IVF cycle before they can get pregnant.
Success rate of IVF can also be measured using the number of times the fertilized ovum (embryo) was transferred into the womans body before pregnancy occurred. Sometimes the embryo has to be transferred more than once.
Another way to assess IVF success rate is the number of times the eggs were collected from the womans ovary.
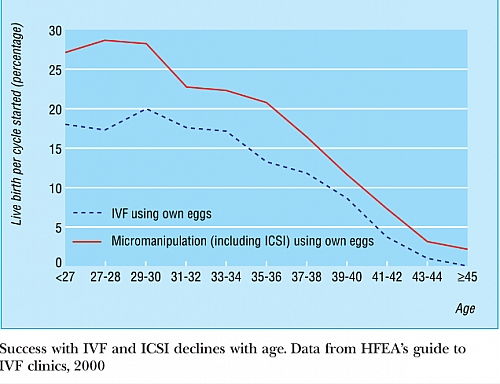
A woman is confirmed to be pregnant following IVF if the concentration of beta human chorionic gonadotropin (hcG) is observed to rise and the gestational sac of the fetus is seen on ultrasound with fetal heart beat present. The rate of live births per IVF cycle is the most important rate compared with just the success rate of pregnancy. The live birth rate is also called the take home baby rate because it measures the number of babies delivered alive following IVF (which is what the couple need and not merely becoming just pregnant). For this reason, the live birth rate is mandatory for all fertility centers/clinics in the United Kingdom to report to the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) which in turn publishes an annual guide to IVF clinics together with the overall success rates, the type of treatment received by the couple and the success rates associated with IVF when the woman is below the age of 38 years.
The chart compares the success rate of IVF with age of the woman. It shows the percentage of life births per cycle of IVF compared with women of ages 27 to 45 years. You can observe that the success rate declines with increasing age; this means the older the woman is, the less likely that she may become pregnant even with IVF. The percentage drops to almost zero when the womans age is 45 years. Out of 100 Women of 39 to 40 years, only about 5 to 10 of them can give birth to a live baby following one cycle of IVF. This decline in the success rate with increasing age especially when the woman passes the age of 40 is due to the lower number of eggs a woman may have as she becomes older with age. The quality of the eggs reduces and the number of eggs that can be collected during IVF reduces even with stimulation with increasing age.
IVF safety to babies
It is unclear if the use of IVF causes congenital abnormalities as this is not yet proven, though it seems there is about 1 to 2 % increase risk of developing congenital malformation.
IVF babies tend to have about 2.6 times risk of being born underweight than the normally conceived babies.
Complications associated with IVF procedure
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Multiple gestation
OHSS is the most important of the effects of IVF on a woman. OHSS signs and symptoms include abdominal pains, abdominal swelling and tendencies of clot formation in the veins and arteries (resulting from haemo-concentration). OHSS may not be avoided completely even with careful measures, some women may still develop it, while others may not; the woman should be monitored for early detection and prompt treatment if OHSS develops.
Women who undergo IVF are at risk of having Ectopic pregnancy but this can be reduced by ultrasound guidance during embryo transfer. Women who are having IVF due to tubal damage are even at more risk of ectopic pregnancy. Women are normally monitored using ultrasound to detect any ectopic pregnancy and treat appropriately.
IVF predisposes a woman to having more than one baby, some may have twins, others triplets. This may seem a blessing but multiple pregnancies with Twins increases the risk of the babies developing cerebral palsy and they are at risk of being born premature.
IVF cost and prices
There is no fixed price to IVF as the cost of treatment varies according to different fertility centers or clinics. Different centers charge according to number of cycles: one, two or more. But it can be as high as 28,000 dollars depending on the quality of service offered.
Some clinics may charge cheaper and may exclude some services such as monitoring, which means you are left with any circumstance that may arise from it. This means if you have complications, you will be charged again to treat it. Whatever IVF center you decide to choose, make sure you have a detailed breakdown of prices from the very first day of consultation to the last day you have your baby in your arms.