Table of Contents
Rabies Virus Description and Classification
Rabies virus is the virus that causes a disease called Rabies. The virus is named after the disease (Rabies). The classic type of rabies virus is the genotype 1 virus and occurs worldwide; there are other genotypes (2 to 7) which have specific distributions across different regions of the word. The rabies virus is a single-stranded RNA virus that belongs to the order called Mononegavirales and Lyssavirus genus. It is classified under the Rhabdoviridae family of viruses and the only member of this family to cause disease in humans.
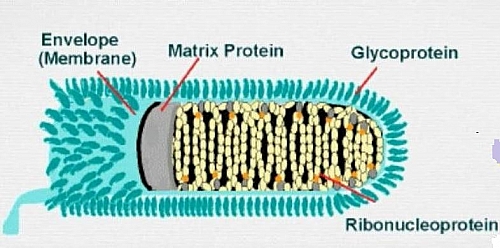
Rabies Virus Structure
The rabies virus measures about 60 by 180nm in size and helical in symmetry and has the shape of a bullet with spikes on the surface of the envelope; these spike-like structures contain glycoproteins which cause the body to produce antibodies that help to neutralize the hemagglutination caused by the rabies virus.
Mode of Transmission of Rabies virus
- The rabies virus is spread to humans by bite from a rabid animal such as dogs this is the major mode of transmission
- Transmission of rabies virus may occur through inhalation of aerosols of secretions from infected bats (this mode of transmission is called the Non-bite transmission and it is rare)
Rabies Virus Characteristics and Facts
- The rabies virus has strong affinity for nervous tissue and the salivary glands causing encephalitis and salivation respectively which are often experience as symptoms in rabies
- The rabies virus is the only medically important member of the rhabdoviridae family of viruses as it is the only virus in the rhabdovirus family that infects human beings.
- The rabies virus is a single-stranded RNA virus with bullet shape
- The virus is surrounded by an envelope made of lipoproteins.
- The genome RNA of the rabies virus has negative polarity; hence, the virion contains an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
- The Rabies virus has a single antigenic type and this is found in the glycoprotein spikes on the envelope
- The rabies virus can infect many animals which serve as the hosts such as mammals (dogs, cats, skunks, coyotes, foxes, raccoons, bats and humans)
Rabies Virus Incubation Period
The incubation period of rabies virus is highly variable and ranges from few weeks to years but the average incubation period is 1 to 3 months
Rabies Virus Replication Cycle
- When the rabies virus enters the human body, it replicates in the muscle cells at the point of entry of the wound
- The rabies virus then penetrates the nerve endings and migrates to the spinal cord and brain
- In the central nervous system (CNS), the rabies virus proliferates again after which it spreads to lungs, kidneys, salivary glands and many other organs of the body.
- The rabies virus replicates by attaching to the acetylcholine receptor on cell surface to gain entry into a cell and then an enzyme called the RNA polymerase synthesizes 5 messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that help in coding the proteins of the rabies virus.
- After the genome of the virus is encoded by RNA polymerase, the RNAs produced are then assembled with proteins of the rabies virus to form the nucelocapsid (covering of the nucleus); the envelope of the rabies virus is formed whenever the virion buds to be released from the infected cell (the virion takes the cell membrane of the infected cell to form its envelope)
Diagnosis of Rabies Virus infection
It is diagnose by skin biopsies and identification of negri bodies from post-mortem brain tissues.
Prevention and Treatment of Rabies Virus infection
Infection by rabies virus is prevented by vaccination of dogs and whenever there is a bite from a suspected rabid animal (an animal with rabies and manifesting the symptoms); the rabies vaccine should be administered immediately. There is currently no cure for rabies when the CNS symptoms have developed and death will be inevitable.